Template:Confidence bounds crow extended rga
Confidence Bounds
In this section, we will present the methods used in RGA to estimate the confidence bounds for the Crow Extended model when applied to developmental testing data. RGA provides two methods to estimate the confidence bounds on demonstrated MTBF and failure intensity, projected MTBF and failure intensity and growth potential MTBF and failure intensity. The two methods are the Fisher Matrix (FM) method and Crow bounds. The Fisher Matrix approach is based on the Fisher Information Matrix and is commonly employed in the reliability field. The Crow bounds were developed by Dr. Larry Crow.
In this appendix, we will present the two methods used in the RGA software to estimate the confidence bounds for the Crow extended model when applied to developmental testing data. The Fisher Matrix approach is based on the Fisher Information Matrix and is commonly employed in the reliability field. The Crow bounds were developed by Dr. Larry Crow.
Bounds on Demonstrated Failure Intensity
Fisher Matrix Bounds
If there are no BC failure modes, the demonstrated failure intensity is
- [math]\displaystyle{ {{\widehat{\lambda }}_{D}}(T)=\tfrac{{{N}_{A}}+{{N}_{BD}}}{T}\,\! }[/math].
Thus:
- [math]\displaystyle{ Var({{\hat{\lambda }}_{D}}(t))=\frac{{{N}_{A}}}{{{T}^{2}}}+\frac{{{N}_{BD}}}{{{T}^{2}}}=\frac{{{\lambda }_{D}}(t)}{T}\,\! }[/math]
and:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{T}\left( \frac{{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{D}}(T)-{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)}{\sqrt{{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)}} \right)\sim N(0,1)\,\! }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ {{\lambda }_{D}}(T)={{\hat{\lambda }}_{D}}(T)+\frac{{{C}^{2}}}{2}\pm \sqrt{{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{D}}(T){{C}^{2}}+\frac{{{C}^{4}}}{4}}\,\! }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ C=\tfrac{{{z}_{1-\alpha /2}}}{\sqrt{T}}\,\! }[/math].
If there are BC failure modes, the demonstrated failure intensity, [math]\displaystyle{ {{\widehat{\lambda }}_{D}}(T)={{\widehat{\lambda }}_{CA}}\,\! }[/math], is actually the instantaneous failure intensity based on all of the data. [math]\displaystyle{ {{\lambda }_{CA}}(T)\,\! }[/math] must be positive; thus, [math]\displaystyle{ \ln {{\lambda }_{CA}}(T)\,\! }[/math] is approximately treated as being normally distributed.
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{\ln {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{CA}}(T)-\ln {{\lambda }_{CA}}(T)}{\sqrt{Var(\ln {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{CA}}(T)})}\sim N(0,1)\,\! }[/math]
The approximate confidence bounds on the instantaneous failure intensity are then estimated from:
- [math]\displaystyle{ CB={{\hat{\lambda }}_{CA}}(T){{e}^{\pm {{z}_{\alpha }}\sqrt{Var({{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{CA}}(T))}/{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{CA}}(T)}}\,\! }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ {{\lambda }_{CA}}(t)=\lambda \beta {{T}^{\beta -1}}\,\! }[/math].
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} Var({{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{CA}}(T))= & {{\left( \frac{\partial {{\lambda }_{CA}}(T)}{\partial \beta } \right)}^{2}}Var(\hat{\beta })+{{\left( \frac{\partial {{\lambda }_{CA}}(T)}{\partial \lambda } \right)}^{2}}Var(\hat{\lambda }) \\ & +2\left( \frac{\partial {{\lambda }_{CA}}(T)}{\partial \beta } \right)\left( \frac{\partial {{\lambda }_{CA}}(T)}{\partial \lambda } \right)cov(\hat{\beta },\hat{\lambda }) \end{align}\,\! }[/math]
The variance calculation is the same as described in the Crow-AMSAA Confidence Bounds appendix.
Crow Bounds
If there are no BC failure modes then:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} {{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{l}}= & {{\widehat{\lambda }}_{D}}(T)\frac{\chi _{(2N,1-\alpha /2)}^{2}}{2N} \\ {{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{u}}= & {{\widehat{\lambda }}_{D}}(T)\frac{\chi _{(2N,\alpha /2)}^{2}}{2N} \end{align}\,\! }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ {{\widehat{\lambda }}_{D}}(T)={{\widehat{\lambda }}_{CA}}\,\! }[/math].
If there are BC modes then the confidence bounds on the demonstrated failure intensity are calculated as presented in the Crow-AMSAA Confidence Bounds appendix.
Bounds on Demonstrated MTBF
Fisher Matrix Bounds
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & MTB{{F}_{{{D}_{L}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{U}}} \\ & MTB{{F}_{{{D}_{U}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{L}}} \end{align}\,\! }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ {{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{L}}\,\! }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ {{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{U}}\,\! }[/math] can be obtained from the equation given above for Bounds on Demonstrated Failure Intensity.
Crow Bounds
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} MTB{{F}_{{{D}_{L}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{U}}} \\ MTB{{F}_{{{D}_{U}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{L}}} \end{align}\,\! }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ {{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{L}}\,\! }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ {{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{U}}\,\! }[/math] can be obtained from the equation given above for Bounds on Demonstrated Failure Intensity.
Bounds on Projected Failure Intensity
Fisher Matrix Bounds
The projected failure intensity [math]\displaystyle{ {{\lambda }_{P}}(T)\,\! }[/math] must be positive; thus, [math]\displaystyle{ \ln {{\lambda }_{P}}(T)\,\! }[/math] is approximately treated as being normally distributed as well:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{\ln {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)-\ln {{\lambda }_{P}}(t)}{\sqrt{Var(\ln {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)})}\sim N(0,1)\,\! }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ CB={{\hat{\lambda }}_{P}}(T){{e}^{\pm {{z}_{\alpha }}\sqrt{Var({{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T))}/{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)}}\,\! }[/math]
where:
- [math]\displaystyle{ {{\hat{\lambda }}_{P}}(T)=\tfrac{{{N}_{A}}}{T}+\underset{i=1}{\overset{M}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,(1-{{d}_{i}})\tfrac{{{N}_{i}}}{T}+\overline{d}\tfrac{M}{T}\bar{\beta }\,\! }[/math] when there are no BC modes.
- [math]\displaystyle{ {{\hat{\lambda }}_{P}}(T)={{\widehat{\lambda }}_{EM}}={{\widehat{\lambda }}_{CA}}-{{\widehat{\lambda }}_{BD}}+\underset{i=1}{\overset{M}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,(1-{{d}_{i}})\tfrac{{{N}_{i}}}{T}+\overline{d}\widehat{h}(T|BD)\,\! }[/math] when there are BC modes.
- [math]\displaystyle{ {{N}_{i}}\,\! }[/math] is the total failure number of the [math]\displaystyle{ {{i}^{th}}\,\! }[/math] distinct BD mode.
You can then get:
- [math]\displaystyle{ Var({{\lambda }_{P}}(T))\approx Var({{\hat{\gamma }}_{GP}})+\mu _{d}^{2}Var(h(T))\approx \frac{{{{\hat{r}}}_{GP}}}{T}+\mu _{d}^{2}Var(h(T))\,\! }[/math]
where:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \hat{h}(T)= & \frac{M}{T}\bar{\beta } \\ Var(\hat{h}(T))= & {{(\frac{M}{T})}^{2}}Var(\bar{\beta })={{(\frac{M}{T})}^{2}}{{(\frac{M}{M-1})}^{2}}Var(\hat{\beta })=\frac{{{M}^{4}}}{{{T}^{2}}{{(M-1)}^{2}}}Var(\hat{\beta }) \end{align}\,\! }[/math]
The [math]\displaystyle{ Var(\hat{\beta })\,\! }[/math] can be obtained from Fisher Matrix based on [math]\displaystyle{ M\,\! }[/math] distinct BD modes.
Crow Bounds
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} {{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{L}}= & {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)+\frac{{{C}^{2}}}{2}-\sqrt{{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)\cdot {{C}^{2}}+\frac{{{C}^{4}}}{4}} \\ {{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{U}}= & {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)+\frac{{{C}^{2}}}{2}+\sqrt{{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)\cdot \ \,{{C}^{2}}+\frac{{{C}^{4}}}{4}} \end{align}\,\! }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ C=\tfrac{{{z}_{1-\alpha /2}}}{\sqrt{T}}\,\! }[/math].
Bounds on Projected MTBF
Fisher Matrix Bounds
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} MTB{{F}_{{{P}_{L}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{U}}} \\ MTB{{F}_{{{P}_{U}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{L}}} \end{align}\,\! }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ {{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{U}}\,\! }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ {{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{L}}\,\! }[/math] can be obtained from the equation given above for Bounds on Projected Failure Intensity.
Crow Bounds
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} MTB{{F}_{{{P}_{L}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{U}}} \\ MTB{{F}_{{{P}_{U}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{L}}} \end{align}\,\! }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ {{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{U}}\,\! }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ {{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{L}}\,\! }[/math] can be obtained from the equation given above for Bounds on Projected Failure Intensity.
Bounds on Growth Potential Failure Intensity
Fisher Matrix Bounds
If there are no BC failure modes, the growth potential failure intensity is
- [math]\displaystyle{ {{\widehat{r}}_{GP}}(T)=\tfrac{{{N}_{A}}}{T}+\underset{i=1}{\overset{M}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,(1-{{d}_{i}})\tfrac{{{N}_{i}}}{T}\,\! }[/math].
Then:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} Var({{\widehat{r}}_{GP}})= & \frac{1}{T}\left[ \frac{{{N}_{A}}}{T}+\underset{i=1}{\overset{M}{\mathop \sum }}\,{{(1-{{d}_{i}})}^{2}}\frac{{{N}_{i}}}{T} \right] \\ \le & \frac{1}{T}\left[ \frac{{{N}_{A}}}{T}+\underset{i=1}{\overset{M}{\mathop \sum }}\,(1-{{d}_{i}})\frac{{{N}_{i}}}{T} \right] \\ = & \frac{{{r}_{GP}}}{T} \end{align}\,\! }[/math]
If there are BC failure modes, the growth potential failure intensity is
- [math]\displaystyle{ {{\widehat{r}}_{GP}}(T)={{\widehat{\lambda }}_{CA}}-{{\widehat{\lambda }}_{BD}}+\underset{i=1}{\overset{M}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,(1-{{d}_{i}})\tfrac{{{N}_{i}}}{T},\,\! }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ Var({{\widehat{r}}_{GP}})\approx \tfrac{{{r}_{GP}}}{T}\,\! }[/math].
Therefore:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{T}\left( \frac{{{{\hat{r}}}_{GP}}-{{r}_{GP}}}{\sqrt{{{r}_{GP}}}} \right)\sim N(0,1)\,\! }[/math]
The confidence bounds on the growth potential failure intensity are as follows:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} {{r}_{L}}= & {{{\hat{r}}}_{GP}}+\frac{{{C}^{2}}}{2}-\sqrt{{{{\hat{r}}}_{GP}}\,{{C}^{2}}+\frac{{{C}^{4}}}{4}} \\ {{r}_{U}}= & {{{\hat{r}}}_{GP}}+\frac{{{C}^{2}}}{2}+\sqrt{{{{\hat{r}}}_{GP}}\,{{C}^{2}}+\frac{{{C}^{4}}}{4}} \end{align}\,\! }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ C=\tfrac{{{z}_{1-\alpha /2}}}{\sqrt{T}}\,\! }[/math].
Crow Bounds
The Crow bounds for the growth potential failure intensity are the same as the Fisher Matrix bounds.
Bounds on Growth Potential MTBF
Fisher Matrix Bounds
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} MTB{{F}_{G{{P}_{L}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{r}_{U}}} \\ MTB{{F}_{G{{P}_{U}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{r}_{L}}} \end{align}\,\! }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ {{r}_{U}}\,\! }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ {{r}_{L}}\,\! }[/math] can be obtained from the equation given above for Bounds on Growth Potential Failure Intensity.
Crow Bounds
The Crow bounds for the growth potential MTBF are the same as the Fisher Matrix bounds.
Bounds on Demonstrated MTBF
Fisher Matrix Bounds
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & MTB{{F}_{{{D}_{L}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{U}}} \\ & MTB{{F}_{{{D}_{U}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{L}}} \end{align} }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ {{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{L}} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ {{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{U}} }[/math] can be obtained from Eqn. (DR).
Crow Bounds
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & MTB{{F}_{{{D}_{L}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{U}}} \\ & MTB{{F}_{{{D}_{U}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{L}}} \end{align} }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ {{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{L}} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ {{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{U}} }[/math] can be obtained from Eqn. (DCR).
Bounds on Projected Failure Intensity
Fisher Matrix Bounds
The projected failure intensity [math]\displaystyle{ {{\lambda }_{P}}(T) }[/math] must be positive, thus [math]\displaystyle{ \ln {{\lambda }_{P}}(T) }[/math] is approximately treated as being normally distributed as well:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{\ln {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)-\ln {{\lambda }_{P}}(t)}{\sqrt{Var(\ln {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)})}\sim N(0,1) }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ CB={{\hat{\lambda }}_{P}}(T){{e}^{\pm {{z}_{\alpha }}\sqrt{Var({{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T))}/{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)}} }[/math]
where:
- • [math]\displaystyle{ {{\hat{\lambda }}_{P}}(T)=\tfrac{{{N}_{A}}}{T}+\underset{i=1}{\overset{M}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,(1-{{d}_{i}})\tfrac{{{N}_{i}}}{T}+\overline{d}\tfrac{M}{T}\bar{\beta } }[/math] when there are no BC modes.
- • [math]\displaystyle{ {{\hat{\lambda }}_{P}}(T)={{\widehat{\lambda }}_{EM}}={{\widehat{\lambda }}_{CA}}-{{\widehat{\lambda }}_{BD}}+\underset{i=1}{\overset{M}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,(1-{{d}_{i}})\tfrac{{{N}_{i}}}{T}+\overline{d}\widehat{h}(T|BD) }[/math] when there are BC modes.
- • [math]\displaystyle{ {{N}_{i}} }[/math] is the total failure number of the [math]\displaystyle{ {{i}^{th}} }[/math] distinct BD mode.
You can then get:
- [math]\displaystyle{ Var({{\lambda }_{P}}(T))\approx Var({{\hat{\gamma }}_{GP}})+\mu _{d}^{2}Var(h(T))\approx \frac{{{{\hat{r}}}_{GP}}}{T}+\mu _{d}^{2}Var(h(T)) }[/math]
- where:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & \hat{h}(T)= & \frac{M}{T}\bar{\beta } \\ & Var(\hat{h}(T))= & {{(\frac{M}{T})}^{2}}Var(\bar{\beta })={{(\frac{M}{T})}^{2}}{{(\frac{M}{M-1})}^{2}}Var(\hat{\beta })=\frac{{{M}^{4}}}{{{T}^{2}}{{(M-1)}^{2}}}Var(\hat{\beta }) \end{align} }[/math]
The [math]\displaystyle{ Var(\hat{\beta }) }[/math] can be obtained from Fisher Matrix based on [math]\displaystyle{ M }[/math] distinct BD modes.
Crow Bounds
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{L}}= & {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)+\frac{{{C}^{2}}}{2}-\sqrt{{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)\cdot {{C}^{2}}+\frac{{{C}^{4}}}{4}} \\ & {{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{U}}= & {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)+\frac{{{C}^{2}}}{2}+\sqrt{{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)\cdot \ \,{{C}^{2}}+\frac{{{C}^{4}}}{4}} \end{align} }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ C=\tfrac{{{z}_{1-\alpha /2}}}{\sqrt{T}} }[/math] .
Bounds on Projected MTBF
Fisher Matrix Bounds
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & MTB{{F}_{{{P}_{L}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{U}}} \\ & MTB{{F}_{{{P}_{U}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{L}}} \end{align} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ {{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{U}} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ {{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{L}} }[/math] can be obtained from Eqn. (extended25).
Crow Bounds
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & MTB{{F}_{{{P}_{L}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{U}}} \\ & MTB{{F}_{{{P}_{U}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{L}}} \end{align} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ {{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{U}} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ {{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{L}} }[/math] can be obtained from Eqn. (PCR).
Bounds on Growth Potential Failure Intensity
Fisher Matrix Bounds
If there are no BC failure modes, the growth potential failure intensity is [math]\displaystyle{ {{\widehat{r}}_{GP}}(T)=\tfrac{{{N}_{A}}}{T}+\underset{i=1}{\overset{M}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,(1-{{d}_{i}})\tfrac{{{N}_{i}}}{T} }[/math] .
- Then:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & Var({{\widehat{r}}_{GP}})= & \frac{1}{T}\left[ \frac{{{N}_{A}}}{T}+\underset{i=1}{\overset{M}{\mathop \sum }}\,{{(1-{{d}_{i}})}^{2}}\frac{{{N}_{i}}}{T} \right] \\ & \le & \frac{1}{T}\left[ \frac{{{N}_{A}}}{T}+\underset{i=1}{\overset{M}{\mathop \sum }}\,(1-{{d}_{i}})\frac{{{N}_{i}}}{T} \right] \\ & = & \frac{{{r}_{GP}}}{T} \end{align} }[/math]
If there are BC failure modes, the growth potential failure intensity is [math]\displaystyle{ {{\widehat{r}}_{GP}}(T)={{\widehat{\lambda }}_{CA}}-{{\widehat{\lambda }}_{BD}}+\underset{i=1}{\overset{M}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,(1-{{d}_{i}})\tfrac{{{N}_{i}}}{T}, }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ Var({{\widehat{r}}_{GP}})\approx \tfrac{{{r}_{GP}}}{T} }[/math] . Therefore:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{T}\left( \frac{{{{\hat{r}}}_{GP}}-{{r}_{GP}}}{\sqrt{{{r}_{GP}}}} \right)\sim N(0,1) }[/math]
The confidence bounds on the growth potential failure intensity are as follows:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{r}_{L}}= & {{{\hat{r}}}_{GP}}+\frac{{{C}^{2}}}{2}-\sqrt{{{{\hat{r}}}_{GP}}\,{{C}^{2}}+\frac{{{C}^{4}}}{4}} \\ & {{r}_{U}}= & {{{\hat{r}}}_{GP}}+\frac{{{C}^{2}}}{2}+\sqrt{{{{\hat{r}}}_{GP}}\,{{C}^{2}}+\frac{{{C}^{4}}}{4}} \end{align} }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ C=\tfrac{{{z}_{1-\alpha /2}}}{\sqrt{T}} }[/math] .
Crow Bounds
The Crow bounds for the growth potential failure intensity are the same as the Fisher Matrix bounds.
Bounds on Growth Potential MTBF
Fisher Matrix Bounds
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & MTB{{F}_{G{{P}_{L}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{r}_{U}}} \\ & MTB{{F}_{G{{P}_{U}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{r}_{L}}} \end{align} }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ {{r}_{U}} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ {{r}_{L}} }[/math] can be obtained from Eqn. (GPR).
Crow Bounds
The Crow bounds for the growth potential MTBF are the same as the Fisher Matrix bounds.
Example 3
Calculate the 2-sided 90% confidence bounds on the demonstrated, projected and growth potential failure intensity for the data in Table 9.1.
Solution
The estimated demonstrated failure intensity is [math]\displaystyle{ {{\widehat{\lambda }}_{D}}(T)=\tfrac{{{N}_{A}}+{{N}_{B}}}{T}=0.1050 }[/math] . Based on this value, the Fisher Matrix confidence bounds for the demonstrated failure intensity at the 90% confidence level are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{L}}= & {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{D}}(T)+\frac{{{C}^{2}}}{2}-\sqrt{{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{D}}(T){{C}^{2}}+\frac{{{C}^{4}}}{4}} \\ & = & 0.08152 \end{align} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{U}}= & {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{D}}(T)+\frac{{{C}^{2}}}{2}+\sqrt{{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{D}}(T){{C}^{2}}+\frac{{{C}^{4}}}{4}} \\ & = & 0.13525 \end{align} }[/math]
The Crow confidence bounds for the demonstrated failure intensity at the 90% confidence level are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{L}}= & {{\widehat{\lambda }}_{D}}(T)\frac{\chi _{(2N,1-\alpha /2)}^{2}}{2N} \\ & = & 0.07985 \\ & {{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{U}}= & {{\widehat{\lambda }}_{D}}(T)\frac{\chi _{(2N,\alpha /2)}^{2}}{2N} \\ & = & 0.13299 \end{align} }[/math]
The projected failure intensity is . Based on this value, the Fisher Matrix confidence bounds at the 90% confidence level for the projected failure intensity are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)]}_{L}}= & {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T){{e}^{{{z}_{\alpha }}\sqrt{Var({{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T))}/{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)}} \\ & = & 0.04902 \end{align} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)]}_{U}}= & {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T){{e}^{-{{z}_{\alpha }}\sqrt{Var({{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T))}/{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)}} \\ & = & 0.08915 \end{align} }[/math]
The Crow confidence bounds for the projected failure intensity are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{L}}= & {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)+\frac{{{C}^{2}}}{2}-\sqrt{{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)\cdot {{C}^{2}}+\frac{{{C}^{4}}}{4}} \\ & = & 0.04807 \\ & {{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{U}}= & {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)+\frac{{{C}^{2}}}{2}+\sqrt{{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)\cdot \ \,{{C}^{2}}+\frac{{{C}^{4}}}{4}} \\ & = & 0.09090 \end{align} }[/math]
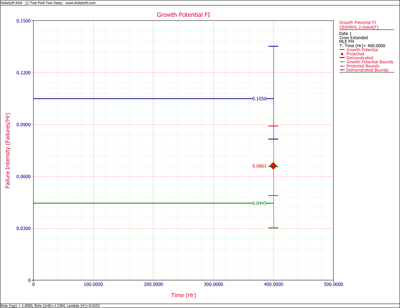
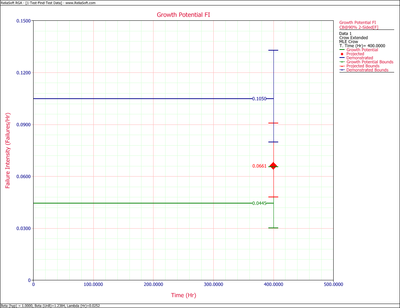
The growth potential failure intensity is [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{r}_{GP} (T) = \left (\frac{N_A}{T} + \sum_{i=1}^M (1-d_i) \tfrac{N_i}{T} \right ) = 0.04455 }[/math].
Based on this value, the Fisher Matrix and Crow confidence bounds at the 90% confidence level for the growth potential failure intensity are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{r}_{L}}= & {{{\hat{r}}}_{GP}}+\frac{{{C}^{2}}}{2}-\sqrt{{{{\hat{r}}}_{GP}}{{C}^{2}}+\frac{{{C}^{4}}}{4}} \\ & = & 0.03020 \\ & {{r}_{U}}= & {{{\hat{r}}}_{GP}}+\frac{{{C}^{2}}}{2}+\sqrt{{{{\hat{r}}}_{GP}}{{C}^{2}}+\frac{{{C}^{4}}}{4}} \\ & = & 0.0656 \end{align} }[/math]
Figure extendedpic7 shows the Fisher Matrix confidence bounds at the 90% confidence level for the demonstrated, projected and growth potential failure intensity. Figure extendedpic8 shows these bounds based on the Crow method.
Example 4
Calculate the 2-sided confidence bounds at the 90% confidence level on the demonstrated, projected and growth potential MTBF for the data in Table 9.3.
Solution
For this example, there are A, BC and BD failure modes, so the estimated demonstrated failure intensity, [math]\displaystyle{ {{\hat{\lambda }}_{D}}(T) }[/math] , is simply the Crow-AMSAA model applied to all A, BC, and BD data.
- [math]\displaystyle{ {{\hat{\lambda }}_{D}}(T)={{\widehat{\lambda }}_{CA}}=\widehat{\lambda }\widehat{\beta }{{T}^{\widehat{\beta }-1}}=0.12744 }[/math]
Therefore, the demonstrated MTBF is:
- [math]\displaystyle{ MTB{{F}_{D}}={{[{{\hat{\lambda }}_{D}}(T)]}^{-1}}=7.84708 }[/math]
Based on this value, the Fisher Matrix confidence bounds for the demonstrated failure intensity at the 90% confidence level are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{L}}= & {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{CA}}(T){{e}^{{{z}_{\alpha }}\sqrt{Var({{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{CA}}(T))}/{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{i}}(T)}} \\ & = & 0.09339 \end{align} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{U}}= & {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{CA}}(T){{e}^{-{{z}_{\alpha }}\sqrt{Var({{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{CA}}(T))}/{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{i}}(T)}} \\ & = & 0.17390 \end{align} }[/math]
The Fisher Matrix confidence bounds for the demonstrated MTBF at the 90% confidence level are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & MTB{{F}_{{{D}_{L}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{U}}} \\ & = & 5.75054 \\ & MTB{{F}_{{{D}_{U}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{L}}} \\ & = & 10.70799 \end{align} }[/math]
The Crow confidence bounds for the demonstrated MTBF at the 90% confidence level are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & MTB{{F}_{{{D}_{L}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{U}}} \\ & = & \frac{1}{{{\widehat{\lambda }}_{D}}(T)\tfrac{{{\chi }^{2}}(2N,\alpha /2)}{2N}} \\ & = & 5.6325 \\ & MTB{{F}_{{{D}_{U}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{D}}(T)]}_{L}}} \\ & = & \frac{1}{{{\widehat{\lambda }}_{D}}(T)\tfrac{{{\chi }^{2}}(2N,1-\alpha /2)}{2N}} \\ & = & 10.8779 \end{align} }[/math]
The projected failure intensity is [math]\displaystyle{ \hat{\lambda}_P (T) = \widehat{\lambda}_{CA} - \widehat{\lambda}_{BD} + \sum_{i=1}^M (1-d_i) \tfrac{N_i}{T} + \bar{d}\widehat{h}(T|BD) = 0.0885 }[/math]. Based on this value, the Fisher Matrix confidence bounds at the 90% confidence level for the projected failure intensity are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{L}}= & {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T){{e}^{{{z}_{\alpha }}\sqrt{Var({{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T))}/{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)}} \\ & = & 0.0681 \end{align} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{U}}= & {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T){{e}^{-{{z}_{\alpha }}\sqrt{Var({{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T))}/{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)}} \\ & = & 0.1152 \end{align} }[/math]
The Fisher Matrix confidence bounds for the projected MTBF at the 90% confidence level are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & MTB{{F}_{{{P}_{L}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{U}}} \\ & = & 8.6818 \\ & MTB{{F}_{{{P}_{U}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{L}}} \\ & = & 14.6926 \end{align} }[/math]
The Crow confidence bounds for the projected failure intensity are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{L}}= & {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)+\frac{{{C}^{2}}}{2}-\sqrt{{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)\cdot \ \,{{C}^{2}}+\frac{{{C}^{4}}}{4}} \\ & = & 0.0672 \\ & {{[{{\lambda }_{P}}(T)]}_{U}}= & {{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)+\frac{{{C}^{2}}}{2}+\sqrt{{{{\hat{\lambda }}}_{P}}(T)\cdot {{C}^{2}}+\frac{{{C}^{4}}}{4}} \\ & = & 0.1166 \end{align} }[/math]
The Crow confidence bounds for the projected MTBF at the 90% confidence level are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & MTB{{F}_{{{P}_{L}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\widehat{\lambda }}_{P}}(T)]}_{U}}} \\ & = & 8.5743 \\ & MTB{{F}_{{{P}_{U}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\widehat{\lambda }}_{P}}(T)]}_{L}}} \\ & = & 14.8769 \end{align} }[/math]
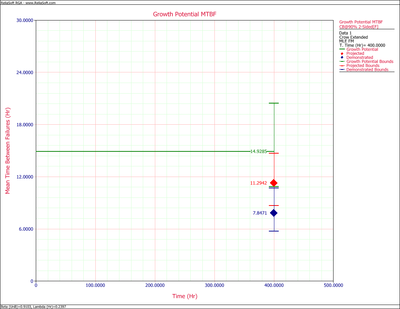
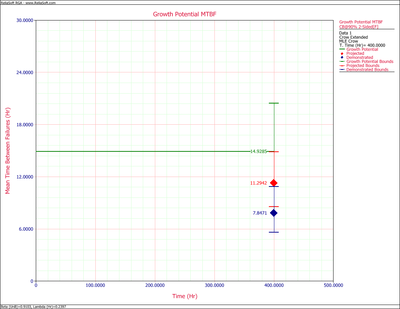
The growth potential failure intensity is [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{\lambda}_{GP} = \widehat{\lambda}_{CA} - \widehat{\lambda}_{BD} + \sum_{i=1}^M (1-d_i) \tfrac{N_i}{T} = 0.0670 }[/math].
[math]\displaystyle{ \hat{\lambda}_P (T) = \widehat{\lambda}_{CA} - \widehat{\lambda}_{BD} + \sum_{i=1}^M (1-d_i) \tfrac{N_i}{T} + \bar{d}\widehat{h}(T|BD) = 0.0885 }[/math].Based on this value, the Fisher Matrix and Crow confidence bounds at the 90% confidence level for the growth potential failure intensity are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{r}_{L}}= & {{{\hat{r}}}_{GP}}+\frac{{{C}^{2}}}{2}-\sqrt{{{{\hat{r}}}_{GP}}{{C}^{2}}+\frac{{{C}^{4}}}{4}} \\ & = & 0.0488 \\ & {{r}_{U}}= & {{{\hat{r}}}_{GP}}+\frac{{{C}^{2}}}{2}+\sqrt{{{{\hat{r}}}_{GP}}{{C}^{2}}+\frac{{{C}^{4}}}{4}} \\ & = & 0.0919 \end{align} }[/math]
The Fisher Matrix and Crow confidence bounds for the growth potential MTBF at the 90% confidence level are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & MTB{{F}_{G{{P}_{L}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{r}_{U}}} \\ & = & 10.8790 \\ & MTB{{F}_{G{{P}_{U}}}}= & \frac{1}{{{r}_{L}}} \\ & = & 20.4855 \end{align} }[/math]
Figure extendedpic9 shows the Fisher Matrix confidence bounds at the 90% confidence level for the demonstrated, projected and growth potential MTBF. Figure extendedpic10 shows these bounds based on the Crow method.