Inverse Power Law (IPL)-Lognormal Model
ALTA_Reference_Examples_Banner.png
|
ALTA_Reference_Examples |
This example compares the results for the IPL life stress relationship with a lognormal distribution.
Reference Case
The data set is from Example 19.10 on page 504 in book Statistical Methods for Reliability Data by Dr. Meeker and Dr. Escobar, John Wiley & Sons, 1998.
Data
A Mylar-Polyurethane Insulating structure was tested under several different voltage settings. The test data is given in the table shown next.
| Time Failed (Hr) | Voltage (kV) | |
|---|---|---|
| 15 | 219 | style="width:50%" |
| 16 | 219 | |
| 36 | 219 | |
| 50 | 219 | |
| 55 | 219 | |
| 95 | 219 | |
| 122 | 219 | |
| 129 | 219 | |
| 625 | 219 | |
| 700 | 219 | |
| 49 | 157.1 | |
| 99 | 157.1 | |
| 154.5 | 157.1 | |
| 180 | 157.1 | |
| 291 | 157.1 | |
| 447 | 157.1 | |
| 510 | 157.1 | |
| 600 | 157.1 | |
| 1656 | 157.1 | |
| 1721 | 157.1 | |
| 188 | 122.4 | |
| 297 | 122.4 | |
| 405 | 122.4 | |
| 744 | 122.4 | |
| 1218 | 122.4 | |
| 1340 | 122.4 | |
| 1715 | 122.4 | |
| 3382 | 122.4 | |
| 606 | 100.3 | |
| 1012 | 100.3 | |
| 2520 | 100.3 | |
| 2610 | 100.3 | |
| 3988 | 100.3 | |
| 4100 | 100.3 | |
| 5025 | 100.3 | |
| 6842 | 100.3 |
Result
The following function is used for the Ln-Mean [math]\displaystyle{ \,\!\mu {}' }[/math]:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \,\!\mu {}'=\beta _{0}+\beta _{1}\times log\left ( V \right ) }[/math]
where V is the voltage and its natural log transform is used in the above life stress relation.
This function can be written in the following way:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \,\!e^{\mu {}'}=e^{\alpha _{0}+\alpha _{1}log\left ( V \right )} }[/math]
The above equation is the general log-linear model in ALTA. In ALTA, the coefficients are denoted by [math]\displaystyle{ \,\!\alpha _{i} }[/math].
In fact, the above model also can be expressed using the traditional IPL (inverse power law) model:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \,\!e^{\mu {}'}=\frac{1}{K\cdot V^{n}} }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ \,\!K=e^{-\alpha _{0}} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \,\!n=-\alpha _{1} }[/math].
In the book, the following results are provided:
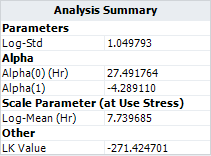
- ML estimations for the model parameters are: [math]\displaystyle{ \,\!\sigma =1.05 }[/math] , [math]\displaystyle{ \,\!\beta _{0}=27.5 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \,\!\beta _{1}=-4.29 }[/math].
- The standard deviation of each parameter are: [math]\displaystyle{ \,\!std\left ( \sigma \right )=0.12 }[/math] , [math]\displaystyle{ \,\!std\left ( \beta _{0} \right )=3.0 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \,\!std\left ( \beta _{1} \right )=0.6 }[/math].
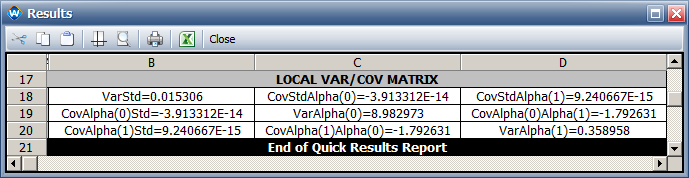
- Therefore, their variances are: [math]\displaystyle{ \,\!Var\left ( \sigma \right )=0.0144 }[/math] , [math]\displaystyle{ \,\!Var\left ( \beta _{0} \right )=9 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \,\!Var\left ( \beta _{1} \right )=0.36 }[/math].
- The log-likelihood value is -271.4.
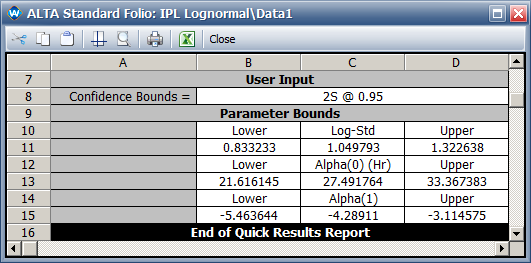
- The 95% two-sided confidence intervals are: for [math]\displaystyle{ \,\!\sigma }[/math] , it is [0.83, 1.32]; for [math]\displaystyle{ \,\!\beta _{0} }[/math] , it is [21.6, 33.4]; and for [math]\displaystyle{ \,\!\beta _{1} }[/math] , it is [-5.46, -3.11].
Results in ALTA
- ML estimations for the model parameters are:
- The variance and covariance matrix for model parameters is:
- The log-likelihood value is -271.4247.
- The 95% two-sided confidence intervals are: