Template:Multiple systems (concurrent operating times): Difference between revisions
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
====Multiple Systems (Concurrent Operating Times)==== | ====Multiple Systems (Concurrent Operating Times)==== | ||
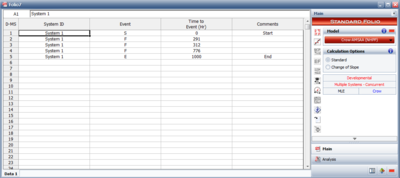
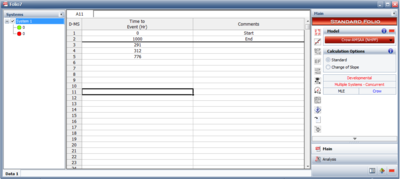
This data type is used for tests where a number of systems are tested and the start, end of failure times are recorded. This data type assumes uniform time accumulation and that the systems are tested simultaneously. As an example, consider the data of two systems shown in the next figure. System 1 begins testing at time equals 0 (with a start event, S) and failures are encountered and corrected at 281, 312 and 776 (with failure events, F). Testing stops at 1000 hours (with an end event, E). System 2 begins testing at time equals 0 and failures are encountered and corrected at 40, 222 and 436. Testing stops at 500 hours. RGA has two options to view this type of data. | This data type is used for tests where a number of systems are tested and the start, end of failure times are recorded. This data type assumes uniform time accumulation and that the systems are tested simultaneously. As an example, consider the data of two systems shown in the next figure. System 1 begins testing at time equals 0 (with a start event, S) and failures are encountered and corrected at 281, 312 and 776 (with failure events, F). Testing stops at 1000 hours (with an end event, E). System 2 begins testing at time equals 0 and failures are encountered and corrected at 40, 222 and 436. Testing stops at 500 hours. RGA has two options to view this type of data. The next two figures show the normal and advanced view. Both figures represent the same data. Note that when entering data within the normal view, each system must be initiated with a start event. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
[[Image:rga3.7.png|thumb|center|400px|Normal view for Multiple Systems (Concurrent Operating Times) data]] | [[Image:rga3.7.png|thumb|center|400px|Normal view for Multiple Systems (Concurrent Operating Times) data]] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
[[Image:rga3.8.png|thumb|center|400px|Advanced view for Multiple Systems (Concurrent Operating Times) data, data for one of two systems displayed]] | [[Image:rga3.8.png|thumb|center|400px|Advanced view for Multiple Systems (Concurrent Operating Times) data, data for one of two systems displayed]] | ||
Revision as of 20:01, 6 June 2012
Multiple Systems (Concurrent Operating Times)
This data type is used for tests where a number of systems are tested and the start, end of failure times are recorded. This data type assumes uniform time accumulation and that the systems are tested simultaneously. As an example, consider the data of two systems shown in the next figure. System 1 begins testing at time equals 0 (with a start event, S) and failures are encountered and corrected at 281, 312 and 776 (with failure events, F). Testing stops at 1000 hours (with an end event, E). System 2 begins testing at time equals 0 and failures are encountered and corrected at 40, 222 and 436. Testing stops at 500 hours. RGA has two options to view this type of data. The next two figures show the normal and advanced view. Both figures represent the same data. Note that when entering data within the normal view, each system must be initiated with a start event.