Template:Grouped failure times: Difference between revisions
(Created page with '====Grouped Failure Times==== This data type is used for tests where the exact failure times are unknown and only the number of failures within a time interval are recorded (e.g.…') |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
This data type is used for tests where the exact failure times are unknown and only the number of failures within a time interval are recorded (e.g. inspection data). For a single system, multiple failures can occur before the operator stops the test. In this case, X number of failures are found after Y hours of test time. Failures X <math>_{1}</math> , X <math>_{2}</math> , X <math>_{3}</math> , etc. could have occurred at any time period up to the termination time, thus exact times for each failure are not available. This is commonly called interval or grouped data. | This data type is used for tests where the exact failure times are unknown and only the number of failures within a time interval are recorded (e.g. inspection data). For a single system, multiple failures can occur before the operator stops the test. In this case, X number of failures are found after Y hours of test time. Failures X <math>_{1}</math> , X <math>_{2}</math> , X <math>_{3}</math> , etc. could have occurred at any time period up to the termination time, thus exact times for each failure are not available. This is commonly called interval or grouped data. | ||
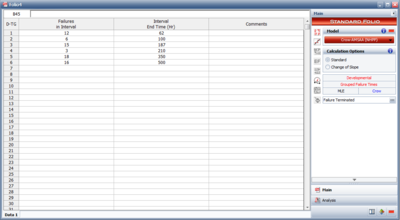
When multiple units are tested, the units are inspected at predetermined time intervals and the number of failed units is recorded. When entering the time at which the failures occurred for grouped data, the time is equal to the total accumulated test time for all of the units being tested. The number of failed units is simply equal to the number of failures that occurred during the current interval. | When multiple units are tested, the units are inspected at predetermined time intervals and the number of failed units is recorded. When entering the time at which the failures occurred for grouped data, the time is equal to the total accumulated test time for all of the units being tested. The number of failed units is simply equal to the number of failures that occurred during the current interval. The next figure shows an example of data entry for grouped data. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
[[Image:rga3.5.png|thumb|center|400px|Grouped Failure Times data]] | [[Image:rga3.5.png|thumb|center|400px|Grouped Failure Times data]] | ||
Revision as of 19:56, 6 June 2012
Grouped Failure Times
This data type is used for tests where the exact failure times are unknown and only the number of failures within a time interval are recorded (e.g. inspection data). For a single system, multiple failures can occur before the operator stops the test. In this case, X number of failures are found after Y hours of test time. Failures X [math]\displaystyle{ _{1} }[/math] , X [math]\displaystyle{ _{2} }[/math] , X [math]\displaystyle{ _{3} }[/math] , etc. could have occurred at any time period up to the termination time, thus exact times for each failure are not available. This is commonly called interval or grouped data.
When multiple units are tested, the units are inspected at predetermined time intervals and the number of failed units is recorded. When entering the time at which the failures occurred for grouped data, the time is equal to the total accumulated test time for all of the units being tested. The number of failed units is simply equal to the number of failures that occurred during the current interval. The next figure shows an example of data entry for grouped data.