Non-Linear Regression: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Kate Racaza (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Kate Racaza (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Reference Example}} | {{Reference Example}} | ||
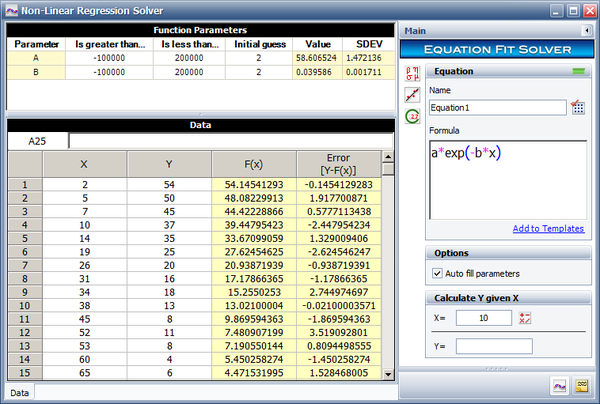
This example | This example validates the results for a non-linear regression by using the Weibull++ Equation Fit Solver tool. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
{{Reference_Example_Heading2}} | {{Reference_Example_Heading2}} | ||
{| {{table}} | {| {{table|10%}} | ||
! | !X | ||
! | !Y | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2||54 | | 2||54 | ||
Latest revision as of 16:25, 28 September 2015
New format available! This reference is now available in a new format that offers faster page load, improved display for calculations and images and more targeted search.
As of January 2024, this Reliawiki page will not continue to be updated. Please update all links and bookmarks to the latest references at Weibull examples and Weibull reference examples.