Template:Bounds on cumulative number of failures camsaa-cb
Bounds on Cumulative Number of Failures
Fisher Matrix Bounds
The cumulative number of failures, [math]\displaystyle{ N(t) }[/math] , must be positive, thus [math]\displaystyle{ \ln N(t) }[/math] is treated as being normally distributed.
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{\ln \hat{N}(t)-\ln N(t)}{\sqrt{Var(\ln \hat{N}(t)})}\ \tilde{\ }\ N(0,1) }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ N(t)=\hat{N}(t){{e}^{\pm {{z}_{\alpha }}\sqrt{Var(\hat{N}(t))}/\hat{N}(t)}} }[/math]
- where:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \hat{N}(t)=\hat{\lambda }{{t}^{{\hat{\beta }}}} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & Var(\hat{N}(t))= & {{\left( \frac{\partial \hat{N}(t)}{\partial \beta } \right)}^{2}}Var(\hat{\beta })+{{\left( \frac{\partial \hat{N}(t)}{\partial \lambda } \right)}^{2}}Var(\hat{\lambda }) \\ & & +2\left( \frac{\partial \hat{N}(t)}{\partial \beta } \right)\left( \frac{\partial \hat{N}(t)}{\partial \lambda } \right)cov(\hat{\beta },\hat{\lambda }) \end{align} }[/math]
The variance calculation is the same as Eqn. (variance1) and:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & \frac{\partial \hat{N}(t)}{\partial \beta }= & \hat{\lambda }{{t}^{{\hat{\beta }}}}\ln t \\ & \frac{\partial \hat{N}(t)}{\partial \lambda }= & {{t}^{{\hat{\beta }}}} \end{align} }[/math]
Crow Bounds
The Crow cumulative number of failure confidence bounds are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{N}_{L}}(T)= & \frac{T}{{\hat{\beta }}}{{\lambda }_{i}}{{(T)}_{L}} \\ & {{N}_{U}}(T)= & \frac{T}{{\hat{\beta }}}{{\lambda }_{i}}{{(T)}_{U}} \end{align} }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ {{\lambda }_{i}}{{(T)}_{L}} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ {{\lambda }_{i}}{{(T)}_{U}} }[/math] can be obtained from Eqn. (amsaac14).
Example 2
Calculate the 90% 2-sided confidence bounds on the cumulative and instantaneous failure intensity for the data from Example 1 given in Table 5.1.
Solution
Fisher Matrix Bounds
Using [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{\beta } }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{\lambda } }[/math] estimated in Example 1, Eqns. (lambda2partial), (beta2partial) and (lambdabeta2partial) are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & \frac{{{\partial }^{2}}\Lambda }{\partial {{\lambda }^{2}}}= & -\frac{22}{{{0.4239}^{2}}}=-122.43 \\ & \frac{{{\partial }^{2}}\Lambda }{\partial {{\beta }^{2}}}= & -\frac{22}{{{0.6142}^{2}}}-0.4239\cdot {{620}^{0.6142}}{{(\ln 620)}^{2}}=-967.68 \\ & \frac{{{\partial }^{2}}\Lambda }{\partial \lambda \partial \beta }= & -{{620}^{0.6142}}\ln 620=-333.64 \end{align} }[/math]
The Fisher Matrix then becomes:
For [math]\displaystyle{ T=620 }[/math] hr, the partial derivatives of the cumulative and instantaneous failure intensities are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & \frac{\partial {{\lambda }_{c}}(T)}{\partial \beta }= & \widehat{\lambda }{{T}^{\widehat{\beta }-1}}\ln (T) \\ & = & 0.4239\cdot {{620}^{-0.3858}}\ln 620 \\ & = & 0.22811336 \\ & \frac{\partial {{\lambda }_{c}}(T)}{\partial \lambda }= & {{T}^{\widehat{\beta }-1}} \\ & = & {{620}^{-0.3858}} \\ & = & 0.083694185 \end{align} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & \frac{\partial {{\lambda }_{i}}(T)}{\partial \beta }= & \widehat{\lambda }{{T}^{\widehat{\beta }-1}}+\widehat{\lambda }\widehat{\beta }{{T}^{\widehat{\beta }-1}}\ln T \\ & = & 0.4239\cdot {{620}^{-0.3858}}+0.4239\cdot 0.6142\cdot {{620}^{-0.3858}}\ln 620 \\ & = & 0.17558519 \end{align} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & \frac{\partial {{\lambda }_{i}}(T)}{\partial \lambda }= & \widehat{\beta }{{T}^{\widehat{\beta }-1}} \\ & = & 0.6142\cdot {{620}^{-0.3858}} \\ & = & 0.051404969 \end{align} }[/math]
Therefore, the variances become:
The cumulative and instantaneous failure intensities at [math]\displaystyle{ T=620 }[/math] hr are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{\lambda }_{c}}(T)= & 0.03548 \\ & {{\lambda }_{i}}(T)= & 0.02179 \end{align} }[/math]
So, at the 90% confidence level and for [math]\displaystyle{ T=620 }[/math] hr, the Fisher Matrix confidence bounds for the cumulative failure intensity are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[{{\lambda }_{c}}(T)]}_{L}}= & 0.02499 \\ & {{[{{\lambda }_{c}}(T)]}_{U}}= & 0.05039 \end{align} }[/math]
The confidence bounds for the instantaneous failure intensity are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[{{\lambda }_{i}}(T)]}_{L}}= & 0.01327 \\ & {{[{{\lambda }_{i}}(T)]}_{U}}= & 0.03579 \end{align} }[/math]
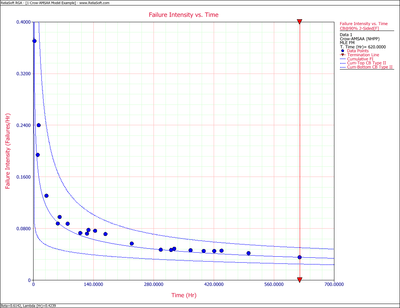
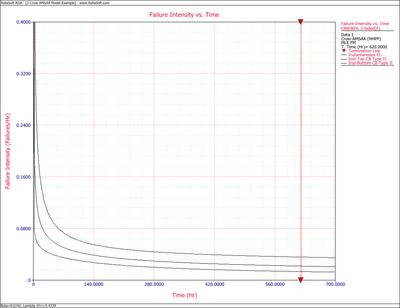
Figures 4fig82 and 4fig83 display plots of the Fisher Matrix confidence bounds for the cumulative and instantaneous failure intensity, respectively.
Crow Bounds
The Crow confidence bounds for the cumulative failure intensity at the 90% confidence level and for [math]\displaystyle{ T=620 }[/math] hr are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[{{\lambda }_{c}}(T)]}_{L}}= & \frac{\chi _{\tfrac{\alpha }{2},2N}^{2}}{2\cdot t} \\ & = & \frac{29.787476}{2*620} \\ & = & 0.02402 \\ & {{[{{\lambda }_{c}}(T)]}_{U}}= & \frac{\chi _{1-\tfrac{\alpha }{2},2N+2}^{2}}{2\cdot t} \\ & = & \frac{62.8296}{2*620} \\ & = & 0.05067 \end{align} }[/math]
The Crow confidence bounds for the instantaneous failure intensity at the 90% confidence level and for [math]\displaystyle{ T=620 }[/math] hr are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[{{\lambda }_{i}}(t)]}_{L}}= & \frac{1}{{{[MTB{{F}_{i}}]}_{U}}} \\ & = & \frac{1}{MTB{{F}_{i}}\cdot U} \\ & = & 0.01179 \end{align} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[{{\lambda }_{i}}(t)]}_{U}}= & \frac{1}{{{[MTB{{F}_{i}}]}_{L}}} \\ & = & \frac{1}{MTB{{F}_{i}}\cdot L} \\ & = & 0.03253 \end{align} }[/math]
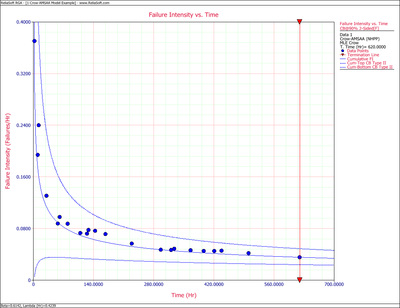
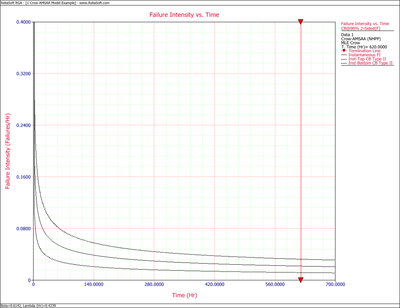
Figures 4fig84 and 4fig85 display plots of the Crow confidence bounds for the cumulative and instantaneous failure intensity, respectively.
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & Var(\widehat{\lambda })= & 0.13519969 \\ & Var(\widehat{\beta })= & 0.017105343 \\ & Cov(\widehat{\beta },\widehat{\lambda })= & -0.046614609 \end{align} }[/math]
Example 3
Calculate the confidence bounds on the cumulative and instantaneous MTBF for the data in Table 5.1.
Solution
Fisher Matrix Bounds
From the previous example:
And for [math]\displaystyle{ T=620 }[/math] hr, the partial derivatives of the cumulative and instantaneous MTBF are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & \frac{\partial {{m}_{c}}(T)}{\partial \beta }= & -\frac{1}{\widehat{\lambda }}{{T}^{1-\widehat{\beta }}}\ln T \\ & = & -\frac{1}{0.4239}{{620}^{0.3858}}\ln 620 \\ & = & -181.23135 \\ & \frac{\partial {{m}_{c}}(T)}{\partial \lambda }= & -\frac{1}{{{\widehat{\lambda }}^{2}}}{{T}^{1-\widehat{\beta }}} \\ & = & -\frac{1}{{{0.4239}^{2}}}{{620}^{0.3858}} \\ & = & -66.493299 \\ & \frac{\partial {{m}_{i}}(T)}{\partial \beta }= & -\frac{1}{\widehat{\lambda }{{\widehat{\beta }}^{2}}}{{T}^{1-\beta }}-\frac{1}{\widehat{\lambda }\widehat{\beta }}{{T}^{1-\widehat{\beta }}}\ln T \\ & = & -\frac{1}{0.4239\cdot {{0.6142}^{2}}}{{620}^{0.3858}}-\frac{1}{0.4239\cdot 0.6142}{{620}^{0.3858}}\ln 620 \\ & = & -369.78634 \\ & \frac{\partial {{m}_{i}}(T)}{\partial \lambda }= & -\frac{1}{{{\widehat{\lambda }}^{2}}\widehat{\beta }}{{T}^{1-\widehat{\beta }}} \\ & = & -\frac{1}{{{0.4239}^{2}}\cdot 0.6142}\cdot {{620}^{0.3858}} \\ & = & -108.26001 \end{align} }[/math]
Therefore, the variances become:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & Var({{\widehat{m}}_{c}}(T))= & {{\left( -181.23135 \right)}^{2}}\cdot 0.017105343+{{\left( -66.493299 \right)}^{2}}\cdot 0.13519969 \\ & & -2\cdot \left( -181.23135 \right)\cdot \left( -66.493299 \right)\cdot 0.046614609 \\ & = & 36.113376 \end{align} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & Var({{\widehat{m}}_{i}}(T))= & {{\left( -369.78634 \right)}^{2}}\cdot 0.017105343+{{\left( -108.26001 \right)}^{2}}\cdot 0.13519969 \\ & & -2\cdot \left( -369.78634 \right)\cdot \left( -108.26001 \right)\cdot 0.046614609 \\ & = & 191.33709 \end{align} }[/math]
So, at 90% confidence level and [math]\displaystyle{ T=620 }[/math] hr, the Fisher Matrix confidence bounds are:
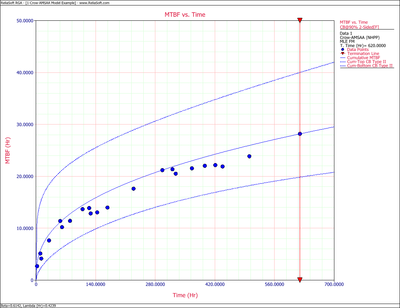
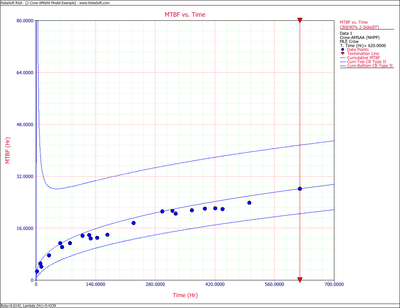
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[{{m}_{c}}(T)]}_{L}}= & {{{\hat{m}}}_{c}}(t){{e}^{-{{z}_{\alpha }}\sqrt{Var({{{\hat{m}}}_{c}}(t))}/{{{\hat{m}}}_{c}}(t)}} \\ & = & 19.84581 \\ & {{[{{m}_{c}}(T)]}_{U}}= & {{{\hat{m}}}_{c}}(t){{e}^{{{z}_{\alpha }}\sqrt{Var({{{\hat{m}}}_{c}}(t))}/{{{\hat{m}}}_{c}}(t)}} \\ & = & 40.01927 \end{align} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[{{m}_{i}}(T)]}_{L}}= & {{{\hat{m}}}_{i}}(t){{e}^{-{{z}_{\alpha }}\sqrt{Var({{{\hat{m}}}_{i}}(t))}/{{{\hat{m}}}_{i}}(t)}} \\ & = & 27.94261 \\ & {{[{{m}_{i}}(T)]}_{U}}= & {{{\hat{m}}}_{i}}(t){{e}^{{{z}_{\alpha }}\sqrt{Var({{{\hat{m}}}_{i}}(t))}/{{{\hat{m}}}_{i}}(t)}} \\ & = & 75.34193 \end{align} }[/math]
Figures 4fig86 and 4fig87 show plots of the Fisher Matrix confidence bounds for the cumulative and instantaneous MTBFs.
Crow Bounds
The Crow confidence bounds for the cumulative MTBF and the instantaneous MTBF at the 90% confidence level and for [math]\displaystyle{ T=620 }[/math] hr are:
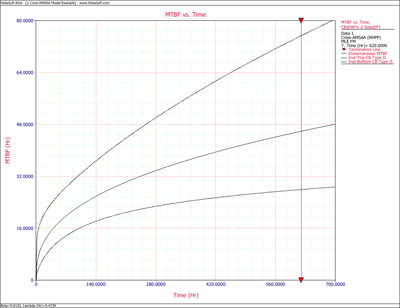
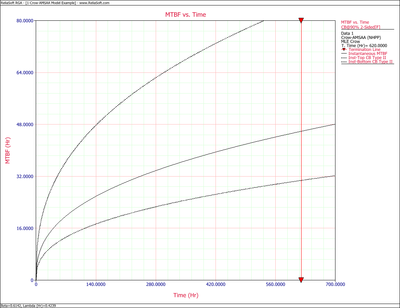
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[{{m}_{c}}(T)]}_{L}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{c}}(T)]}_{U}}} \\ & = & 20.5023 \\ & {{[{{m}_{c}}(T)]}_{U}}= & \frac{1}{{{[{{\lambda }_{c}}(T)]}_{L}}} \\ & = & 41.6282 \end{align} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{[MTB{{F}_{i}}]}_{L}}= & MTB{{F}_{i}}\cdot {{\Pi }_{1}} \\ & = & 30.7445 \\ & {{[MTB{{F}_{i}}]}_{U}}= & MTB{{F}_{i}}\cdot {{\Pi }_{2}} \\ & = & 84.7972 \end{align} }[/math]
Figures 4fig88 and 4fig89 show plots of the Crow confidence bounds for the cumulative and instantaneous MTBF.
Confidence bounds can also be obtained on the parameters [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{\beta } }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{\lambda } }[/math] . For Fisher Matrix confidence bounds:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{\beta }_{L}}= & \hat{\beta }{{e}^{{{z}_{\alpha }}\sqrt{Var(\hat{\beta })}/\hat{\beta }}} \\ & = & 0.4325 \\ & {{\beta }_{U}}= & \hat{\beta }{{e}^{-{{z}_{\alpha }}\sqrt{Var(\hat{\beta })}/\hat{\beta }}} \\ & = & 0.8722 \end{align} }[/math]
- and:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{\lambda }_{L}}= & \hat{\lambda }{{e}^{{{z}_{\alpha }}\sqrt{Var(\hat{\lambda })}/\hat{\lambda }}} \\ & = & 0.1016 \\ & {{\lambda }_{U}}= & \hat{\lambda }{{e}^{-{{z}_{\alpha }}\sqrt{Var(\hat{\lambda })}/\hat{\lambda }}} \\ & = & 1.7691 \end{align} }[/math]
For Crow confidence bounds:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{\beta }_{L}}= & 0.4527 \\ & {{\beta }_{U}}= & 0.9350 \end{align} }[/math]
- and:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & {{\lambda }_{L}}= & 0.2870 \\ & {{\lambda }_{U}}= & 0.5827 \end{align} }[/math]