1P-Exponential MLE Solution for Interval Data: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Kate Racaza (talk | contribs) (Created page with '{{Reference Example}} Compares the MLE solution, likelihood ratio bound and Fisher Matrix bound for a 1-parameter exponential distribution with interval data. {{Reference_Exam…') |
Kate Racaza (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
* Based on lognormal approximation, the confidence interval is [496, 660]. The calculation is: | * Based on lognormal approximation, the confidence interval is [496, 660]. The calculation is: | ||
<math>\,\ | ::<math>\begin{alignat}{2} | ||
[\theta_{L},\theta_{U}]&= \hat{\theta}exp(\pm 1.96\times \frac{se_{\hat{\theta}}}{\hat{\theta}})\\ | |||
&=\left [572.3\times exp(-1.96\times\tfrac{41.72}{572.3}),572.3\times exp(1.96\times\tfrac{41.72}{572.3})\right]\\ | |||
&= [496,660]\\ | |||
\end{alignat}</math> | |||
{{Reference_Example_Heading4}} | {{Reference_Example_Heading4}} | ||
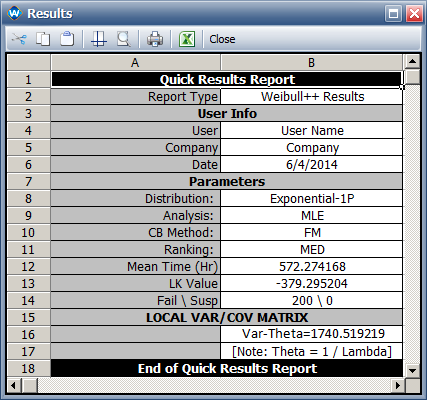
The ML estimator for <math>\theta\,\!</math> and its variance are 572.27 and 1637.489, respectively. They are given below. | |||
[[Image:1PE_interval_data.png|center]] | |||
The ML estimator for <math>\theta\,\!</math> and the variance are the same as the values given in the book. The following calculation provides the step by step analytical results for calculating the variance of <math>\theta\,\!</math>. | |||
The 95% 2-sided confidence interval for <math>\theta\,\!</math> are: | |||
* Based on the likelihood ratio (Select LRB for the confidence bound), the confidence interval is | |||
Revision as of 18:37, 4 June 2014
New format available! This reference is now available in a new format that offers faster page load, improved display for calculations and images and more targeted search.
As of January 2024, this Reliawiki page will not continue to be updated. Please update all links and bookmarks to the latest references at Weibull examples and Weibull reference examples.