Logistic Model - Auto Transmission Example: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Kate Racaza (talk | contribs) Created page with '<noinclude>{{Banner RGA Examples}} ''This example appears in the Reliability Growth and Repairable System Analysis Reference book''. </noinclude> The following tabl…' |
Chris Kahn (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
The following table presents the reliabilities observed monthly for an automobile transmission that was tested for one year. | The following table presents the reliabilities observed monthly for an automobile transmission that was tested for one year. | ||
#Find a Logistic reliability growth curve that best represents the data. | |||
#Plot it comparatively with the raw data. | |||
#If design changes continue to be incorporated and the testing continues, when will the reliability goal of 99% be achieved? | |||
#If design changes continue to be incorporated and the testing continues, what will be the attainable reliability at the end of January the following year? | |||
{|border="1" align="center" style="border-collapse: collapse;" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="5" | {|border="1" align="center" style="border-collapse: collapse;" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="5" | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
'''Solution ''' | '''Solution ''' | ||
<ol> | |||
<li>The next figure shows the estimated parameters. | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
: | [[Image:rga8.7.png|thumb|center|650px|Entered data and the estimated Logistic parameters.]] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
</li> | |||
< | <li>The next figure displays the Reliability vs. Time plot. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
[[Image:rga8.8.png|thumb|center|400px|Reliability vs. Time plot.]] | [[Image:rga8.8.png|thumb|center|400px|Reliability vs. Time plot.]] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
</li> | |||
<li>Using the QCP, the next figure displays when the reliability goal of 99% will be achieved. | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
[[Image:rga8.9.png|thumb|center|400px|When the reliability goal of 99% will be achieved.]] | [[Image:rga8.9.png|thumb|center|400px|When the reliability goal of 99% will be achieved.]] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
</li> | |||
<li>The last figure shows the reliability at the end of January the following year (i.e., after 20 months of testing and development). | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
[[Image:rga8.10.png|thumb|center|400px|The reliability at the end of the following January (month=20)]] | [[Image:rga8.10.png|thumb|center|400px|The reliability at the end of the following January (month=20)]] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
</li> | |||
</ol> | |||
Revision as of 23:41, 31 January 2014
 |
New format available! This reference is now available in a new format that offers faster page load, improved display for calculations and images and more targeted search.
As of January 2024, this Reliawiki page will not continue to be updated. Please update all links and bookmarks to the latest references at RGA examples and RGA reference examples.
This example appears in the Reliability Growth and Repairable System Analysis Reference book.
The following table presents the reliabilities observed monthly for an automobile transmission that was tested for one year.
- Find a Logistic reliability growth curve that best represents the data.
- Plot it comparatively with the raw data.
- If design changes continue to be incorporated and the testing continues, when will the reliability goal of 99% be achieved?
- If design changes continue to be incorporated and the testing continues, what will be the attainable reliability at the end of January the following year?
| Month | Observed Reliability(%) |
|---|---|
| June | 22 |
| July | 26 |
| August | 30 |
| September | 34 |
| October | 45 |
| November | 58 |
| December | 68 |
| January | 79 |
| February | 85 |
| March | 89 |
| April | 92 |
| May | 95 |
Solution
- The next figure shows the estimated parameters.
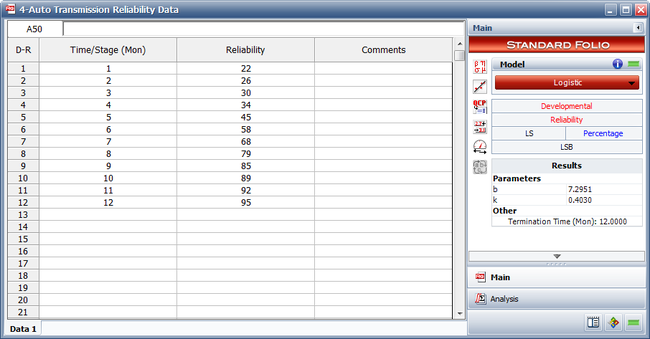
Entered data and the estimated Logistic parameters.
- The next figure displays the Reliability vs. Time plot.
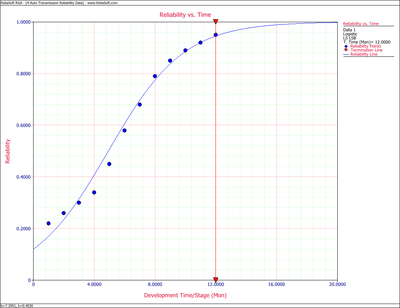
Reliability vs. Time plot.
- Using the QCP, the next figure displays when the reliability goal of 99% will be achieved.
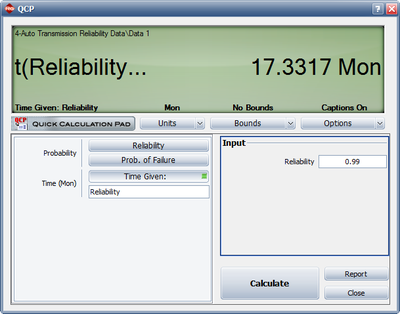
When the reliability goal of 99% will be achieved.
- The last figure shows the reliability at the end of January the following year (i.e., after 20 months of testing and development).
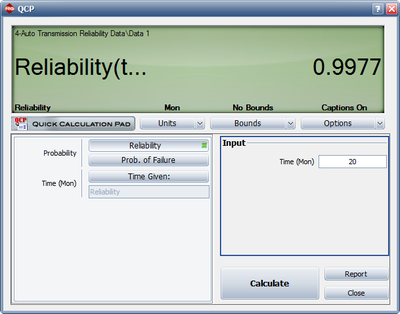
The reliability at the end of the following January (month=20)