Template:Complete Data: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Created page with '====Complete Data==== Complete data means that the value of each sample unit is observed or known. For example, if we had to compute the average test score for a sample of ten s…' |
Kate Racaza (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
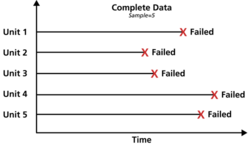
Complete data means that the value of each sample unit is observed or known. For example, if we had to compute the average test score for a sample of ten students, complete data would consist of the known score for each student. Likewise in the case of life data analysis, our data set (if complete) would be composed of the times-to-failure of all units in our sample. For example, if we tested five units and they all failed (and their times-to-failure were recorded), we would then have complete information as to the time of each failure in the sample. | Complete data means that the value of each sample unit is observed or known. For example, if we had to compute the average test score for a sample of ten students, complete data would consist of the known score for each student. Likewise in the case of life data analysis, our data set (if complete) would be composed of the times-to-failure of all units in our sample. For example, if we tested five units and they all failed (and their times-to-failure were recorded), we would then have complete information as to the time of each failure in the sample. | ||
<br> | |||
[[Image:complete data.png|center|250px|]] | |||
<br> | |||
Revision as of 10:35, 2 July 2012
Complete Data
Complete data means that the value of each sample unit is observed or known. For example, if we had to compute the average test score for a sample of ten students, complete data would consist of the known score for each student. Likewise in the case of life data analysis, our data set (if complete) would be composed of the times-to-failure of all units in our sample. For example, if we tested five units and they all failed (and their times-to-failure were recorded), we would then have complete information as to the time of each failure in the sample.