Template:Gumbel probability paper: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Probability Paper== | ==Probability Paper== | ||
The form of the Gumbel probability paper is based on a linearization of the <math>cdf</math> . From | The form of the Gumbel probability paper is based on a linearization of the <math>cdf</math> . From the unreliabililty equation, we know: | ||
::<math>z=\ln (-\ln (1-F))</math> | ::<math>z=\ln (-\ln (1-F))</math> | ||
using the equation for ''z'', we get: | |||
: | ::<math>\frac{t-\mu }{\sigma }=\ln (-\ln (1-F))</math> | ||
: | Then: | ||
::<math>\ln (-\ln (1-F))=-\frac{\mu }{\sigma }+\frac{1}{\sigma }t</math> | |||
Now let: | |||
::<math>y=\ln (-\ln (1-F))</math> | ::<math>y=\ln (-\ln (1-F))</math> | ||
::<math>x=t</math> | |||
::<math>x= | |||
and: | |||
::<math>\begin{align} | ::<math>\begin{align} | ||
| Line 35: | Line 29: | ||
::<math>y=a+bx</math> | ::<math>y=a+bx</math> | ||
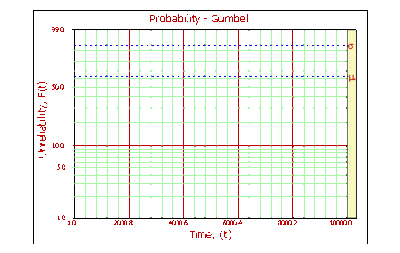
The Gumbel probability paper resulting from this linearized <math>cdf</math> function is shown next. | The Gumbel probability paper resulting from this linearized <math>cdf</math> function is shown next. | ||
| Line 41: | Line 34: | ||
[[Image:probabilitygumbel.gif|thumb|center|400px| ]] | [[Image:probabilitygumbel.gif|thumb|center|400px| ]] | ||
For <math>z=0</math> , <math> | For <math>z=0</math> , <math>t=\mu </math> and <math>R(t)={{e}^{-{{e}^{0}}}}\approx 0.3678</math> (63.21% unreliability). For <math>z=1</math> , <math>\sigma =T-\mu </math> and <math>R(t)={{e}^{-{{e}^{1}}}}\approx 0.0659.</math> To read <math>\mu </math> from the plot, find the time value that corresponds to the intersection of the probability plot with the 63.21% unreliability line. To read <math>\sigma </math> from the plot, find the time value that corresponds to the intersection of the probability plot with the 93.40% unreliability line, then take the difference between this time value and the <math>\mu </math> value. | ||
Revision as of 18:36, 20 February 2012
Probability Paper
The form of the Gumbel probability paper is based on a linearization of the [math]\displaystyle{ cdf }[/math] . From the unreliabililty equation, we know:
- [math]\displaystyle{ z=\ln (-\ln (1-F)) }[/math]
using the equation for z, we get:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{t-\mu }{\sigma }=\ln (-\ln (1-F)) }[/math]
Then:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \ln (-\ln (1-F))=-\frac{\mu }{\sigma }+\frac{1}{\sigma }t }[/math]
Now let:
- [math]\displaystyle{ y=\ln (-\ln (1-F)) }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ x=t }[/math]
and:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & a= & -\frac{\mu }{\sigma } \\ & b= & \frac{1}{\sigma } \end{align} }[/math]
which results in the linear equation of:
- [math]\displaystyle{ y=a+bx }[/math]
The Gumbel probability paper resulting from this linearized [math]\displaystyle{ cdf }[/math] function is shown next.
For [math]\displaystyle{ z=0 }[/math] , [math]\displaystyle{ t=\mu }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ R(t)={{e}^{-{{e}^{0}}}}\approx 0.3678 }[/math] (63.21% unreliability). For [math]\displaystyle{ z=1 }[/math] , [math]\displaystyle{ \sigma =T-\mu }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ R(t)={{e}^{-{{e}^{1}}}}\approx 0.0659. }[/math] To read [math]\displaystyle{ \mu }[/math] from the plot, find the time value that corresponds to the intersection of the probability plot with the 63.21% unreliability line. To read [math]\displaystyle{ \sigma }[/math] from the plot, find the time value that corresponds to the intersection of the probability plot with the 93.40% unreliability line, then take the difference between this time value and the [math]\displaystyle{ \mu }[/math] value.