Template:Example: Normal Distribution RRY: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
{|align="center" border=1 cellspacing=1 | {|align="center" border=1 cellspacing=1 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2" style="text-align:center"|Table | |colspan="2" style="text-align:center"|Table 9.1 -The test data | ||
|- | |- | ||
!Data point index | !Data point index | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
Construct a table like the one shown next. | Construct a table like the one shown next. | ||
<center><math>\overset{{}}{\mathop{\text{Table | <center><math>\overset{{}}{\mathop{\text{Table 9}\text{.2 - Least Squares Analysis}}}\,</math></center> | ||
<center><math>\begin{matrix} | <center><math>\begin{matrix} | ||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
:*The <math>{{y}_{i}}</math> values were obtained from standardized normal distribution's area tables by entering for <math>F(z)</math> and getting the corresponding <math>z</math> value ( <math>{{y}_{i}}</math> ). As with the median rank values, these standard normal values can be obtained with the Quick Statistical Reference. | :*The <math>{{y}_{i}}</math> values were obtained from standardized normal distribution's area tables by entering for <math>F(z)</math> and getting the corresponding <math>z</math> value ( <math>{{y}_{i}}</math> ). As with the median rank values, these standard normal values can be obtained with the Quick Statistical Reference. | ||
Given the values in Table | Given the values in Table 9.2, calculate <math>\widehat{a}</math> and <math>\widehat{b}</math> using: | ||
::<math>\begin{align} | ::<math>\begin{align} | ||
| Line 104: | Line 104: | ||
The preceding example can be repeated using Weibull++ . | The preceding example can be repeated using Weibull++ . | ||
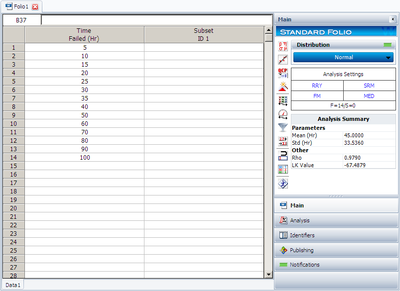
:*Create a new folio for Times-to-Failure data, and enter the data given in Table | :*Create a new folio for Times-to-Failure data, and enter the data given in Table 9.1. | ||
:*Choose Normal from the Distributions list. | :*Choose Normal from the Distributions list. | ||
:*Go to the Analysis page and select Rank Regression on Y (RRY). | :*Go to the Analysis page and select Rank Regression on Y (RRY). | ||
Revision as of 23:27, 10 February 2012
Normal Distribution RRY Example
Fourteen units were reliability tested and the following life test data were obtained:
| Table 9.1 -The test data | |
| Data point index | Time-to-failure |
|---|---|
| 1 | 5 |
| 2 | 10 |
| 3 | 15 |
| 4 | 20 |
| 5 | 25 |
| 6 | 30 |
| 7 | 35 |
| 8 | 40 |
| 9 | 50 |
| 10 | 60 |
| 11 | 70 |
| 12 | 80 |
| 13 | 90 |
| 14 | 100 |
Assuming the data follow a normal distribution, estimate the parameters and determine the correlation coefficient, [math]\displaystyle{ \rho }[/math] , using rank regression on Y.
Solution
Construct a table like the one shown next.
- The median rank values ( [math]\displaystyle{ F({{t}_{i}}) }[/math] ) can be found in rank tables, available in many statistical texts, or they can be estimated by using the Quick Statistical Reference in Weibull++.
- The [math]\displaystyle{ {{y}_{i}} }[/math] values were obtained from standardized normal distribution's area tables by entering for [math]\displaystyle{ F(z) }[/math] and getting the corresponding [math]\displaystyle{ z }[/math] value ( [math]\displaystyle{ {{y}_{i}} }[/math] ). As with the median rank values, these standard normal values can be obtained with the Quick Statistical Reference.
Given the values in Table 9.2, calculate [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{a} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{b} }[/math] using:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & \widehat{b}= & \frac{\underset{i=1}{\overset{14}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,{{T}_{i}}{{y}_{i}}-(\underset{i=1}{\overset{14}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,{{T}_{i}})(\underset{i=1}{\overset{14}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,{{y}_{i}})/14}{\underset{i=1}{\overset{14}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,T_{i}^{2}-{{(\underset{i=1}{\overset{14}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,{{T}_{i}})}^{2}}/14} \\ & & \\ & \widehat{b}= & \frac{365.2711-(630)(0)/14}{40,600-{{(630)}^{2}}/14}=0.02982 \end{align} }[/math]
and:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{a}=\overline{y}-\widehat{b}\overline{T}=\frac{\underset{i=1}{\overset{N}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,{{y}_{i}}}{N}-\widehat{b}\frac{\underset{i=1}{\overset{N}{\mathop{\sum }}}\,{{t}_{i}}}{N} }[/math]
or:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{a}=\frac{0}{14}-(0.02982)\frac{630}{14}=-1.3419 }[/math]
Therefore:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{\sigma}=\frac{1}{\hat{b}}=\frac{1}{0.02982}=33.5367 }[/math]
and:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{\mu }=-\widehat{a}\cdot \widehat{\sigma }=-(-1.3419)\cdot 33.5367\simeq 45 }[/math]
or [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{\mu }=45 }[/math] hours [math]\displaystyle{ . }[/math]
The correlation coefficient can be estimated using:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{\rho }=0.979 }[/math]
The preceding example can be repeated using Weibull++ .
- Create a new folio for Times-to-Failure data, and enter the data given in Table 9.1.
- Choose Normal from the Distributions list.
- Go to the Analysis page and select Rank Regression on Y (RRY).
- Click the Calculate icon located on the Main page.
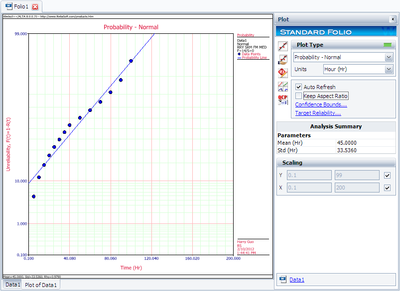
The probability plot is shown next.