Optimal Test Plan for Two Stresses: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Kate Racaza (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Kate Racaza (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Reference Example| | {{Reference Example|{{Banner ALTA Reference Examples}}}} | ||
This example | This example validates the results for the 3 level optimum test plan with two stresses in ALTA. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
{{Reference_Example_Heading2}} | {{Reference_Example_Heading2}} | ||
A Weibull distribution with the following life stress relationship is used. | A Weibull distribution with the following life-stress relationship is used. | ||
::<math>ln(\eta)=\beta_{0}+\beta_{1} \times log(vpm) + \beta_{2} \frac{11605}{temp}\,\!</math> | ::<math>ln(\eta)=\beta_{0}+\beta_{1} \times log(vpm) + \beta_{2} \frac{11605}{temp}\,\!</math> | ||
where ''temp'' is the temperature in | where ''temp'' is the temperature in Kelvins and ''vpm'' is the voltage stress in volts/mm. The planning values for the model parameters for the test plan are: | ||
::<math>\beta = \frac{1}{\sigma} = 1.485\,\!</math> , <math>\beta_{1} = 12.28\,\!</math> and <math>\beta_{2} = 0.3878\,\!</math> | ::<math>\beta = \frac{1}{\sigma} = 1.485\,\!</math> , <math>\beta_{0} = 58.173\,\!</math> , <math>\beta_{1} = -12.28\,\!</math> and <math>\beta_{2} = 0.3878\,\!</math> | ||
These planning values are given on page 535. | These planning values are given on page 535. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
The use condition stress values are vpm = 80 volts/mm and temp = 120°C (393.15°K). | The use condition stress values are vpm = 80 volts/mm and temp = 120°C (393.15°K). | ||
The highest stress values that can be used in the test are vpm = 200 volts/mm and temp = 260°C (533.15°K). | The highest stress values that can be used in the test are: vpm = 200 volts/mm and temp = 260°C (533.15°K). | ||
A total of 170 units | A total of 170 units will tested for 1,000 hours. Three combinations of temperature and voltage levels can be used in the test. The objectives of the test plan are to: | ||
* Determine the three stress combinations used in the test. | * Determine the three stress combinations that should be used in the test. | ||
* Determine the number of test units at each stress combination. | * Determine the number of test units at each stress combination. | ||
Tests will be conducted using the created test plan. The failure data from the test will be used to estimate the model parameters | Tests will be conducted using the created test plan. The failure data from the test will be used to estimate the model parameters, which are then used to predict the B10 life at vpm = 80 volts/mm and temp = 120°C. Therefore, we need a test plan that will minimize the estimation variance of the B10 life at the given usage stress level. | ||
{{Reference_Example_Heading3}} | |||
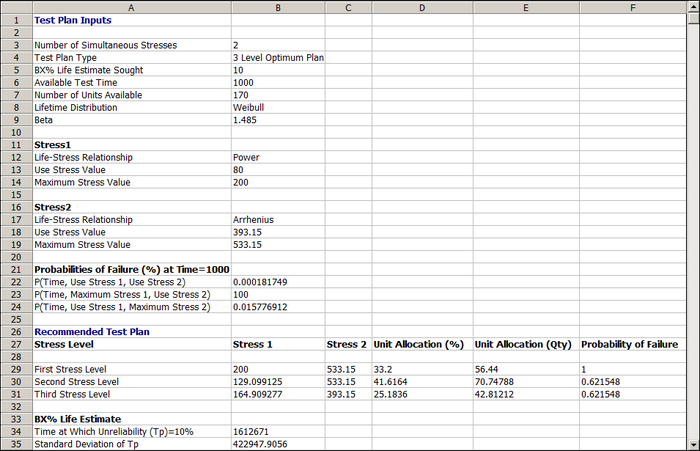
The three stress combinations and the number of test units at each of them are: | |||
:* 62 units should be tested at 124 volts and 260°C (533.15°K) | |||
:* 42 units should be tested at 159 volts and 120°C (393.15°K) | |||
:* 66 units should be tested at 200 volts and 260°C (533.15°K) | |||
Based on this test plan, the estimated standard error for the B10 life at vpm = 80 volts/mm and temp = 120°C is <math>Ase \left[log(\hat{t}_{0.1}(50))\right]\,\!</math> = 0.3670 . | |||
The standard error is calculated from the result in Table 20.6, as shown next: | |||
{{ | ::<math>\frac{n}{\sigma^{2}}Var\left[log(\hat{t}_{0.1}(50)) \right] = 50.5\,\!</math> | ||
Since n = 170 and <math>\frac{1}{\sigma^{2}} = \beta^{2}\,\!</math> = 2.205229, so <math>Var\left [log(\hat{t}_{0.1}(50)) \right]\,\!</math> = 0.1347. Therefore, <math>Ase \left[log(\hat{t}_{0.1}(50)) \right]\,\!</math> = 0.3670. | |||
| Line 54: | Line 58: | ||
The probabilities of failure (%) at time | The probabilities of failure (%) at time 1000 are calculated based on the test planning values. For example, at the use stress of voltage and at the maximum stress of temperature, the life characteristic is: | ||
::<math>\begin{align} | ::<math>\begin{align} | ||
| Line 65: | Line 68: | ||
Therefore, <math>\eta\,\!</math> = 363269. The probability of failure is calculated by: | Therefore, <math>\eta\,\!</math> = 363269. The probability of failure is calculated by: | ||
::<math>\begin{align} | ::<math>\begin{align} | ||
| Line 74: | Line 76: | ||
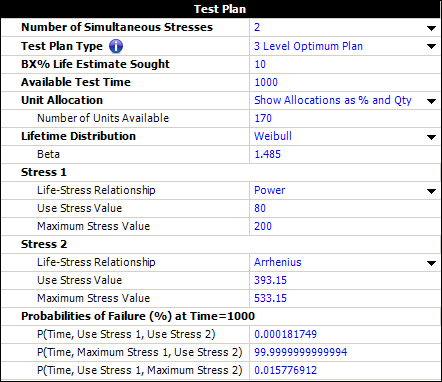
The | The resulting test plan in ALTA is shown below. | ||
[[Image: Optimal plan test plan.png|center|700px]] | [[Image: Optimal plan test plan.png|center|700px]] | ||
The test plan shows that: | The test plan shows that (starting at row 29 in the picture above): | ||
* The first stress level | * The first stress level should be a combination of 200 volts and 260°C (533.15°K) and about 56 units should be tested at that level. | ||
* The second stress level | * The second stress level should be a combination of 129 volts and 260°C (533.15°K) and about 71 units should be tested at that level. | ||
* The third stress level (row 31) should be a combination of 165 volts and 120°C (393.15°K) and about 43 units should be tested at that level. | * The third stress level (row 31) should be a combination of 165 volts and 120°C (393.15°K) and about 43 units should be tested at that level. | ||
| Line 93: | Line 95: | ||
The above results are different from the results given in the book. In the following discussion, a simulation study is conducted to check the results obtained from ALTA. | The above results are different from the results given in the book. In the following discussion, a simulation study is conducted to check the results obtained from ALTA. | ||
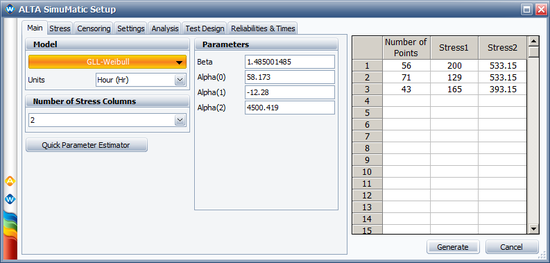
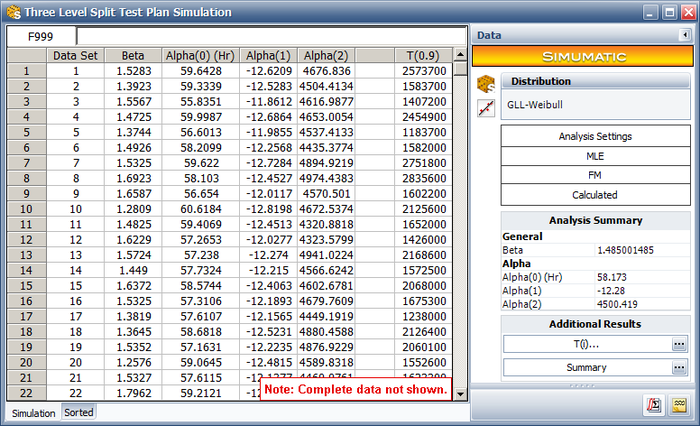
We will use the SimuMatic utility to evaluate the test plan. The following picture shows the settings used in the Main tab of SimuMatic (with <math>\alpha_{1} = \beta_{1} \times 11605\,\!</math>): | '''Using SimuMatic to Evaluate the Test Plan''' | ||
We will use the ALTA SimuMatic utility to evaluate the test plan. The following picture shows the settings used in the Main tab of SimuMatic (with <math>\alpha_{1} = \beta_{1} \times 11605\,\!</math>): | |||
[[Image: Optimal plan simumatic1.png|center|550px]] | [[Image: Optimal plan simumatic1.png|center|550px]] | ||
The rest of the SimuMatic | The rest of the settings in SimuMatic are as follows: | ||
* Stress tab: | * Stress tab: | ||
| Line 109: | Line 112: | ||
* Settings tab | * Settings tab | ||
::Seed = '''10''', Precision = '''4''', Number of data sets = '''1000''' | ::Seed = '''10''', Precision = '''4''', Number of data sets = '''1000''' | ||
* Reliabilities and Times | * Reliabilities and Times tab | ||
::Reliability value = '''0.9''' | ::Reliability value = '''0.9''' | ||
| Line 118: | Line 121: | ||
We take the | We take the natural log of the B10 life (the last column) and calculate its standard deviation. The calculated standard deviation is 0.2629. This is very close to the analytical solution from the ALTA test plan tool, where the standard deviation is 0.2623. | ||
This standard deviation is smaller than the standard deviation given by the test plan in the book. Therefore, the test plan generated in ALTA is better than the test plan given in the book in terms of minimizing the estimation variance of the B10 life. | This standard deviation is smaller than the standard deviation given by the test plan in the book. Therefore, the test plan generated in ALTA is better than the test plan given in the book in terms of minimizing the estimation variance of the B10 life. | ||
Latest revision as of 18:24, 28 September 2015
New format available! This reference is now available in a new format that offers faster page load, improved display for calculations and images and more targeted search.
As of January 2024, this Reliawiki page will not continue to be updated. Please update all links and bookmarks to the latest references at ALTA examples and ALTA reference examples.