Template:Event codes rga: Difference between revisions
(Created page with '===Event Codes=== The Multiple Systems with Event Codes data type analyzed with the Crow Extended model uses a column to indicate the types of events that occurred during a test …') |
Lisa Hacker (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
The analysis is based on the equivalent system that combines the operating hours of all the systems. | The analysis is based on the equivalent system that combines the operating hours of all the systems. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | |||
===Transferring to Other Data Types=== | |||
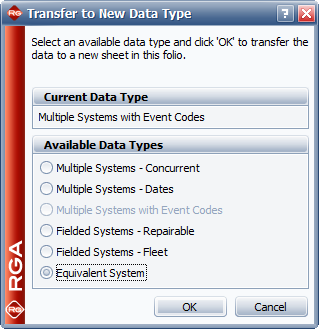
RGA provides the capability to transfer a Multiple Systems with Event Codes data sheet to various other data types. The following picture shows the available data types that the data sheet can be converted into. When selecting to transfer to an equivalent single system, the data sheet is converted to a Crow Extended - Continuous Evaluation data sheet. | |||
[[Image:rga9.23.png|thumb|center|400px|Transferring the Multiple Systems with Event Codes data sheet to an equivalent single system using the Crow Extended-Continuous Evaluation model.]] | |||
<br> | |||
The Crow Extended - Continuous Evaluation model is designed for analyzing data across multiple test phases, while considering the data for all phases as one data set. This model is covered in detail in Chapter 10 and familiarity with that model is necessary for the discussion presented in this section. | |||
<br> | |||
When using the Crow Extended - Continuous Evaluation model to transfer the data sheet from Multiple Systems with Event Codes to an equivalent single system, the following rules are used (in addition to the five basic rules presented earlier for calculating the equivalent single system): | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
:*BD modes in the Crow Extended data sheet become BD modes in the equivalent single system of the Crow Extended - Continuous Evaluation data sheet. | |||
:*BC modes in the Crow Extended data sheet become BD modes in the equivalent single system of the Crow Extended - Continuous Evaluation data sheet. These BD modes will have associated implemented fixes (I events). Implemented fixes (I events) for BC modes in the Crow Extended data sheet become implemented fixes (I events) for the converted BD modes in the equivalent single system of the Crow Extended - Continuous Evaluation data sheet. | |||
:*If an implemented fix (I event) occurred at the same time as the failure and was implemented at that exact time across all systems, then this becomes a BC mode in the equivalent single system. If the fixes (I events) were not all implemented at the same time or if the fix was not implemented on all systems at the failure time, then this becomes a BD mode in the equivalent single system. | |||
<br> | |||
The next figure shows the transferred equivalent single system Crow Extended - Continuous Evaluation data sheet from the Multiple Systems with Event Codes data sheet for the data from the [[Equivalent Single System example]] given above. | |||
[[Image:rga9.24.png|thumb|center|400px|The transferred equivalent single system Crow Extended- Continuous Evaluation data sheet from the Multiple Systems with Event Codes data sheet of Figure 9.15.]] | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 02:07, 23 August 2012
Event Codes
The Multiple Systems with Event Codes data type analyzed with the Crow Extended model uses a column to indicate the types of events that occurred during a test phase. Within RGA, event codes are entered within the Event column of the Multiple Systems with Event Codes data sheets.
The possible event codes that can be used in the analysis are:
I: denotes that a certain BC failure mode has been corrected at the specific time; in other words, a fix has been implemented. For this data type, each BC mode must have an associated I event. The I event is essentially a timestamp for when the fix was implemented during the test.
Q: indicates that the failure was due to a quality issue. An example of this might be a failure caused by a bolt not being tightened down properly. You have the option to decide whether or not to include quality issues in the analysis. This option can be specified by checking or clearing the Include Q Events checkbox under Event Code Options on the Analysis tab.
P: indicates that the failure was due to a performance issue. You can determine whether or not to include performance issues in the analysis. This option can be specified by checking or clearing the Include P Events checkbox under Event Code Options on the Analysis tab.
X: indicates that you wish to exclude the data point from the analysis. An "X" can be placed in front of any existing event code (e.g. XF to exclude a particular failure time) or entered by itself. This row of data will then not be included in the analysis.
S: indicates the system start time. This event code is only selectable in the Normal View.
F: indicates a failure time.
E: indicates the system end time. This event code is only selectable in the Normal View.
The analysis is based on the equivalent system that combines the operating hours of all the systems.
Transferring to Other Data Types
RGA provides the capability to transfer a Multiple Systems with Event Codes data sheet to various other data types. The following picture shows the available data types that the data sheet can be converted into. When selecting to transfer to an equivalent single system, the data sheet is converted to a Crow Extended - Continuous Evaluation data sheet.
The Crow Extended - Continuous Evaluation model is designed for analyzing data across multiple test phases, while considering the data for all phases as one data set. This model is covered in detail in Chapter 10 and familiarity with that model is necessary for the discussion presented in this section.
When using the Crow Extended - Continuous Evaluation model to transfer the data sheet from Multiple Systems with Event Codes to an equivalent single system, the following rules are used (in addition to the five basic rules presented earlier for calculating the equivalent single system):
- BD modes in the Crow Extended data sheet become BD modes in the equivalent single system of the Crow Extended - Continuous Evaluation data sheet.
- BC modes in the Crow Extended data sheet become BD modes in the equivalent single system of the Crow Extended - Continuous Evaluation data sheet. These BD modes will have associated implemented fixes (I events). Implemented fixes (I events) for BC modes in the Crow Extended data sheet become implemented fixes (I events) for the converted BD modes in the equivalent single system of the Crow Extended - Continuous Evaluation data sheet.
- If an implemented fix (I event) occurred at the same time as the failure and was implemented at that exact time across all systems, then this becomes a BC mode in the equivalent single system. If the fixes (I events) were not all implemented at the same time or if the fix was not implemented on all systems at the failure time, then this becomes a BD mode in the equivalent single system.
The next figure shows the transferred equivalent single system Crow Extended - Continuous Evaluation data sheet from the Multiple Systems with Event Codes data sheet for the data from the Equivalent Single System example given above.