Template:Characteristics of the gamma distribution: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with '===Characteristics of the Gamma Distribution=== Some of the specific characteristics of the gamma distribution are the following: For <math>k>1</math> : :• As <math>T\to 0,\…') |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
===Characteristics of the Gamma Distribution=== | ===Characteristics of the Gamma Distribution=== | ||
Some of the specific characteristics of the gamma distribution are the following: | Some of the specific characteristics of the gamma distribution are the following: | ||
For <math>k>1</math> : | For <math>k>1</math> : | ||
:• As <math> | :• As <math>t\to 0,\infty </math> , <math>f(t)\to 0.</math> | ||
:• <math>f( | :• <math>f(t)</math> increases from 0 to the mode value and decreases thereafter. | ||
:• If <math>k\le 2</math> then <math>pdf</math> has one inflection point at <math> | :• If <math>k\le 2</math> then <math>pdf</math> has one inflection point at <math>t={{e}^{\mu }}\sqrt{k-1}(</math> <math>\sqrt{k-1}+1).</math> | ||
:• If <math>k>2</math> then <math>pdf</math> has two inflection points for <math>T={{e}^{\mu }}\sqrt{k-1}(</math> <math>\sqrt{k-1}\pm 1).</math> | :• If <math>k>2</math> then <math>pdf</math> has two inflection points for <math>T={{e}^{\mu }}\sqrt{k-1}(</math> <math>\sqrt{k-1}\pm 1).</math> | ||
:• For a fixed <math>k</math> , as <math>\mu </math> increases, the <math>pdf</math> starts to look more like a straight angle. | :• For a fixed <math>k</math> , as <math>\mu </math> increases, the <math>pdf</math> starts to look more like a straight angle. | ||
As <math> | As <math>t\to \infty ,\lambda (t)\to \tfrac{1}{{{e}^{\mu }}}.</math> | ||
[[Image:ldaGD10.1.gif|thumb|center|400px| ]] | [[Image:ldaGD10.1.gif|thumb|center|400px| ]] | ||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
For <math>0<k<1</math> : | For <math>0<k<1</math> : | ||
:• As <math> | :• As <math>t\to 0</math> , <math>f(t)\to \infty .</math> | ||
:• As <math> | :• As <math>t\to \infty ,f(t)\to 0.</math> | ||
:• As <math> | :• As <math>t\to \infty ,\lambda (t)\to \tfrac{1}{{{e}^{\mu }}}.</math> | ||
:• The <math>pdf</math> decreases monotonically and is convex. | :• The <math>pdf</math> decreases monotonically and is convex. | ||
:• As <math>\mu </math> increases, the <math>pdf</math> gets stretched out to the right and its height decreases, while maintaining its shape. | :• As <math>\mu </math> increases, the <math>pdf</math> gets stretched out to the right and its height decreases, while maintaining its shape. | ||
Revision as of 22:22, 14 February 2012
Characteristics of the Gamma Distribution
Some of the specific characteristics of the gamma distribution are the following:
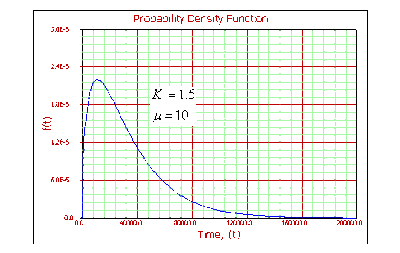
For [math]\displaystyle{ k\gt 1 }[/math] :
- • As [math]\displaystyle{ t\to 0,\infty }[/math] , [math]\displaystyle{ f(t)\to 0. }[/math]
- • [math]\displaystyle{ f(t) }[/math] increases from 0 to the mode value and decreases thereafter.
- • If [math]\displaystyle{ k\le 2 }[/math] then [math]\displaystyle{ pdf }[/math] has one inflection point at [math]\displaystyle{ t={{e}^{\mu }}\sqrt{k-1}( }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{k-1}+1). }[/math]
- • If [math]\displaystyle{ k\gt 2 }[/math] then [math]\displaystyle{ pdf }[/math] has two inflection points for [math]\displaystyle{ T={{e}^{\mu }}\sqrt{k-1}( }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{k-1}\pm 1). }[/math]
- • For a fixed [math]\displaystyle{ k }[/math] , as [math]\displaystyle{ \mu }[/math] increases, the [math]\displaystyle{ pdf }[/math] starts to look more like a straight angle.
As [math]\displaystyle{ t\to \infty ,\lambda (t)\to \tfrac{1}{{{e}^{\mu }}}. }[/math]
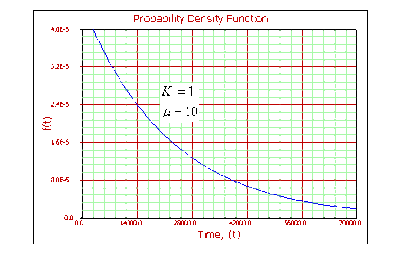
For [math]\displaystyle{ k=1 }[/math] :
- • Gamma becomes the exponential distribution.
- • As [math]\displaystyle{ T\to 0 }[/math] , [math]\displaystyle{ f(T)\to \tfrac{1}{{{e}^{\mu }}}. }[/math]
- • As [math]\displaystyle{ T\to \infty ,f(T)\to 0. }[/math]
- • The [math]\displaystyle{ pdf }[/math] decreases monotonically and is convex.
- • [math]\displaystyle{ \lambda (T)\equiv \tfrac{1}{{{e}^{\mu }}} }[/math] . [math]\displaystyle{ \lambda (T) }[/math] is constant.
- • The mode does not exist.
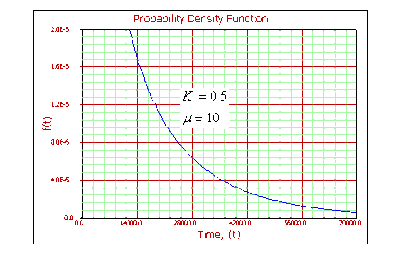
For [math]\displaystyle{ 0\lt k\lt 1 }[/math] :
- • As [math]\displaystyle{ t\to 0 }[/math] , [math]\displaystyle{ f(t)\to \infty . }[/math]
- • As [math]\displaystyle{ t\to \infty ,f(t)\to 0. }[/math]
- • As [math]\displaystyle{ t\to \infty ,\lambda (t)\to \tfrac{1}{{{e}^{\mu }}}. }[/math]
- • The [math]\displaystyle{ pdf }[/math] decreases monotonically and is convex.
- • As [math]\displaystyle{ \mu }[/math] increases, the [math]\displaystyle{ pdf }[/math] gets stretched out to the right and its height decreases, while maintaining its shape.
- • As [math]\displaystyle{ \mu }[/math] decreases, the [math]\displaystyle{ pdf }[/math] shifts towards the left and its height increases.
- • The mode does not exist.