RGA Data Types: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
{{discrete data}} | {{discrete data}} | ||
===Multi-Phase Data=== | |||
Reliability data can be analyzed across multiple phases. This is useful when an overall reliability growth program is planned and involves multiple test phases. | |||
====(Multi-Phase) Failure Times Data==== | |||
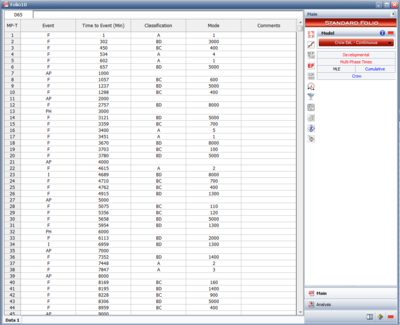
This data type can be used for tests that span multiple phases and the exact failure times are recorded. Figure CECETF shows an example of multi-phase failure times data, where the different events signify failures (F), test phases (PH) or analysis points (AP). | |||
[[Image:rga3.15.png|thumb|center|400px|Multi-phase failure times data]] | |||
====(Multi-Phase) Grouped Failure Times Data==== | |||
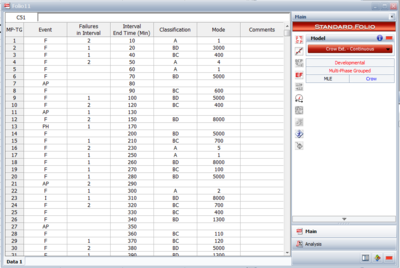
This data type can be used for tests that span multiple phases and the exact failure times are unknown. Only the number of failures within a time interval are recorded, as shown in Figure CECErouped. | |||
[[Image:rga3.16.png|thumb|center|400px|Multi-phase grouped failure times data]] | |||
====(Multi-Phase) Mixed Data==== | |||
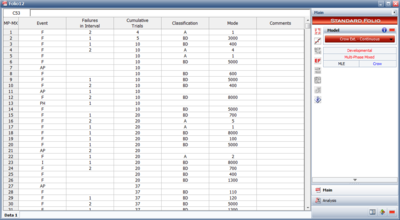
This data type can be used for tests that span multiple phases and it allows for configuration in groups, individual trial by trial, or a mixed combination of individual trials and configurations of more than one trial. An example of this data type can be seen in Figure Multi-phase mixed data. | |||
[[Image:rga3.17.png|thumb|center|400px|Multi-phase mixed data]] | |||
====Models for Multi-Phase Data==== | |||
The Crow Extended - Continuous Evaluation model is used to analyze data across multiple phases and is presented in Chapter 10. | |||
===Reliability Data=== | ===Reliability Data=== | ||
Revision as of 00:38, 24 August 2012
Reliability growth analysis can be conducted using different data types. This chapter explores and examines the possible data schemes and outlines the available models for each data type. The data types for developmental testing (traditional reliability growth analysis) will be discussed first. Then we will discuss the data types that support the use of RGA models for analyzing fielded systems (either for repairable systems analysis or fleet data analysis).
Developmental Testing Data Types
Reliability growth analysis can be conducted using different data types. This chapter explores and examines the possible data schemes and outlines the available models for each data type. The data types for developmental testing (traditional reliability growth analysis) will be discussed first. Then we will discuss the data types that support the use of RGA models for analyzing fielded systems (either for repairable systems analysis or fleet data analysis).
Developmental Testing Data Types
Template loop detected: Template:Time-to-failure data
Template loop detected: Template:Discrete data
Multi-Phase Data
Reliability data can be analyzed across multiple phases. This is useful when an overall reliability growth program is planned and involves multiple test phases.
(Multi-Phase) Failure Times Data
This data type can be used for tests that span multiple phases and the exact failure times are recorded. Figure CECETF shows an example of multi-phase failure times data, where the different events signify failures (F), test phases (PH) or analysis points (AP).
(Multi-Phase) Grouped Failure Times Data
This data type can be used for tests that span multiple phases and the exact failure times are unknown. Only the number of failures within a time interval are recorded, as shown in Figure CECErouped.
(Multi-Phase) Mixed Data
This data type can be used for tests that span multiple phases and it allows for configuration in groups, individual trial by trial, or a mixed combination of individual trials and configurations of more than one trial. An example of this data type can be seen in Figure Multi-phase mixed data.
Models for Multi-Phase Data
The Crow Extended - Continuous Evaluation model is used to analyze data across multiple phases and is presented in Chapter 10.
Reliability Data
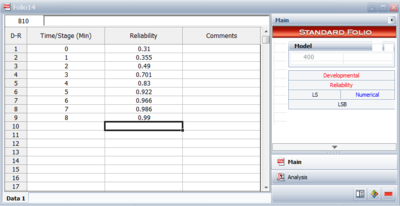
Reliability data consists of entering the reliability of the equipment at different times or stages. An example is shown in Figure Reliability. In this case, the process is monitored at pre-defined time intervals and the reliability is recorded. The reliability can be computed by a simple ratio of the number of units still functioning vs. the number of units that entered the test stage or by using Life Data Analysis and related methods (e.g. Weibull analysis).
Models for Reliability Data
The following models can be used to analyze reliability data sets. Models and examples using different data types are discussed in later chapters.
1) Lloyd-Lipow (Chapter 6)
2) Gompertz and Modified Gompertz (Chapter 7)
3) Logistic (Chapter 8)
Fielded Systems
Fielded systems are systems that are used by customers in the field and for which failure information is not derived from an in-house test. This type of data is analogous to warranty data. The data types available for fielded systems data entry are:
- Repairable Systems
- Fleet
Repairable Systems
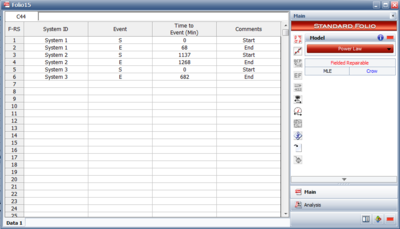
Repairable Systems data is identical in format to the Multiple Systems (Concurrent Operating Times) data. It also can be entered in the normal or advanced view. Figure Repair illustrates a sample data set. In repairable systems, the purpose of the analysis is not to evaluate reliability growth but rather to obtain reliability estimates for the system, including expected number of failures, reliability at a given time, and so forth.
Models for Repairable Systems Data
The following models can be used to analyze repairable systems data. Models and examples using different data types are discussed in Chapter 13.
1) Power Law
2) Crow Extended
Fleet Data
This data type is used to analyze the entire population (fleet). The data entry for this data type is similar to the data entry for repairable systems; however, the overall data analysis is again different. In repairable systems, the reliability of a single system can be tracked and quantified, whereas in a fleet analysis, data from the entire fleet as a whole is analyzed. The figure below presents an example of data entered for fleet analysis. Models for Fleet Data
The following models can be used to analyze fleet data. Models and examples using different data types are discussed in later chapters.
- Crow-AMSAA (NHPP)
- Crow Extended
<INSERT PIC>
Reliability growth analysis can be conducted using different data types. This chapter explores and examines the possible data schemes and outlines the available models for each data type. The data types for developmental testing (traditional reliability growth analysis) will be discussed first. Then we will discuss the data types that support the use of RGA models for analyzing fielded systems (either for repairable systems analysis or fleet data analysis).
Developmental Testing Data Types
Template loop detected: Template:Time-to-failure data
Template loop detected: Template:Discrete data
Multi-Phase Data
Reliability data can be analyzed across multiple phases. This is useful when an overall reliability growth program is planned and involves multiple test phases.
(Multi-Phase) Failure Times Data
This data type can be used for tests that span multiple phases and the exact failure times are recorded. Figure CECETF shows an example of multi-phase failure times data, where the different events signify failures (F), test phases (PH) or analysis points (AP).
(Multi-Phase) Grouped Failure Times Data
This data type can be used for tests that span multiple phases and the exact failure times are unknown. Only the number of failures within a time interval are recorded, as shown in Figure CECErouped.
(Multi-Phase) Mixed Data
This data type can be used for tests that span multiple phases and it allows for configuration in groups, individual trial by trial, or a mixed combination of individual trials and configurations of more than one trial. An example of this data type can be seen in Figure Multi-phase mixed data.
Models for Multi-Phase Data
The Crow Extended - Continuous Evaluation model is used to analyze data across multiple phases and is presented in Chapter 10.
Reliability Data
Reliability data consists of entering the reliability of the equipment at different times or stages. An example is shown in Figure Reliability. In this case, the process is monitored at pre-defined time intervals and the reliability is recorded. The reliability can be computed by a simple ratio of the number of units still functioning vs. the number of units that entered the test stage or by using Life Data Analysis and related methods (e.g. Weibull analysis).
Models for Reliability Data
The following models can be used to analyze reliability data sets. Models and examples using different data types are discussed in later chapters.
1) Lloyd-Lipow (Chapter 6)
2) Gompertz and Modified Gompertz (Chapter 7)
3) Logistic (Chapter 8)
Fielded Systems
Fielded systems are systems that are used by customers in the field and for which failure information is not derived from an in-house test. This type of data is analogous to warranty data. The data types available for fielded systems data entry are:
- Repairable Systems
- Fleet
Repairable Systems
Repairable Systems data is identical in format to the Multiple Systems (Concurrent Operating Times) data. It also can be entered in the normal or advanced view. Figure Repair illustrates a sample data set. In repairable systems, the purpose of the analysis is not to evaluate reliability growth but rather to obtain reliability estimates for the system, including expected number of failures, reliability at a given time, and so forth.
Models for Repairable Systems Data
The following models can be used to analyze repairable systems data. Models and examples using different data types are discussed in Chapter 13.
1) Power Law
2) Crow Extended
Fleet Data
This data type is used to analyze the entire population (fleet). The data entry for this data type is similar to the data entry for repairable systems; however, the overall data analysis is again different. In repairable systems, the reliability of a single system can be tracked and quantified, whereas in a fleet analysis, data from the entire fleet as a whole is analyzed. The figure below presents an example of data entered for fleet analysis. Models for Fleet Data
The following models can be used to analyze fleet data. Models and examples using different data types are discussed in later chapters.
- Crow-AMSAA (NHPP)
- Crow Extended
<INSERT PIC>
Multi-Phase Data
Reliability data can be analyzed across multiple phases. This is useful when an overall reliability growth program is planned and involves multiple test phases.
(Multi-Phase) Failure Times Data
This data type can be used for tests that span multiple phases and the exact failure times are recorded. Figure CECETF shows an example of multi-phase failure times data, where the different events signify failures (F), test phases (PH) or analysis points (AP).
(Multi-Phase) Grouped Failure Times Data
This data type can be used for tests that span multiple phases and the exact failure times are unknown. Only the number of failures within a time interval are recorded, as shown in Figure CECErouped.
(Multi-Phase) Mixed Data
This data type can be used for tests that span multiple phases and it allows for configuration in groups, individual trial by trial, or a mixed combination of individual trials and configurations of more than one trial. An example of this data type can be seen in Figure Multi-phase mixed data.
Models for Multi-Phase Data
The Crow Extended - Continuous Evaluation model is used to analyze data across multiple phases and is presented in Chapter 10.
Reliability Data
Reliability data consists of entering the reliability of the equipment at different times or stages. An example is shown in Figure Reliability. In this case, the process is monitored at pre-defined time intervals and the reliability is recorded. The reliability can be computed by a simple ratio of the number of units still functioning vs. the number of units that entered the test stage or by using Life Data Analysis and related methods (e.g. Weibull analysis).
Models for Reliability Data
The following models can be used to analyze reliability data sets. Models and examples using different data types are discussed in later chapters.
1) Lloyd-Lipow (Chapter 6)
2) Gompertz and Modified Gompertz (Chapter 7)
3) Logistic (Chapter 8)
Fielded Systems
Fielded systems are systems that are used by customers in the field and for which failure information is not derived from an in-house test. This type of data is analogous to warranty data. The data types available for fielded systems data entry are:
- Repairable Systems
- Fleet
Repairable Systems
Repairable Systems data is identical in format to the Multiple Systems (Concurrent Operating Times) data. It also can be entered in the normal or advanced view. Figure Repair illustrates a sample data set. In repairable systems, the purpose of the analysis is not to evaluate reliability growth but rather to obtain reliability estimates for the system, including expected number of failures, reliability at a given time, and so forth.
Models for Repairable Systems Data
The following models can be used to analyze repairable systems data. Models and examples using different data types are discussed in Chapter 13.
1) Power Law
2) Crow Extended
Fleet Data
This data type is used to analyze the entire population (fleet). The data entry for this data type is similar to the data entry for repairable systems; however, the overall data analysis is again different. In repairable systems, the reliability of a single system can be tracked and quantified, whereas in a fleet analysis, data from the entire fleet as a whole is analyzed. The figure below presents an example of data entered for fleet analysis. Models for Fleet Data
The following models can be used to analyze fleet data. Models and examples using different data types are discussed in later chapters.
- Crow-AMSAA (NHPP)
- Crow Extended
<INSERT PIC>